Creatine is not just for athletes—it boosts brain function, energy, and supports healthy aging.
For decades, creatine has been the most researched and widely used supplement in sports nutrition. Known primarily for muscle and strength gains, recent studies show that creatine also offers cognitive, neurological, and anti-aging benefits that most people don’t know about.
Understanding the science behind creatine matters because it goes far beyond the gym. Students, professionals, seniors, and women can also benefit from its wide-ranging effects. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the full spectrum of creatine’s benefits, debunk common myths, explain dosage and safety, and show you why creatine deserves a spot in your daily health routine.
What Is Creatine and How Does It Work?
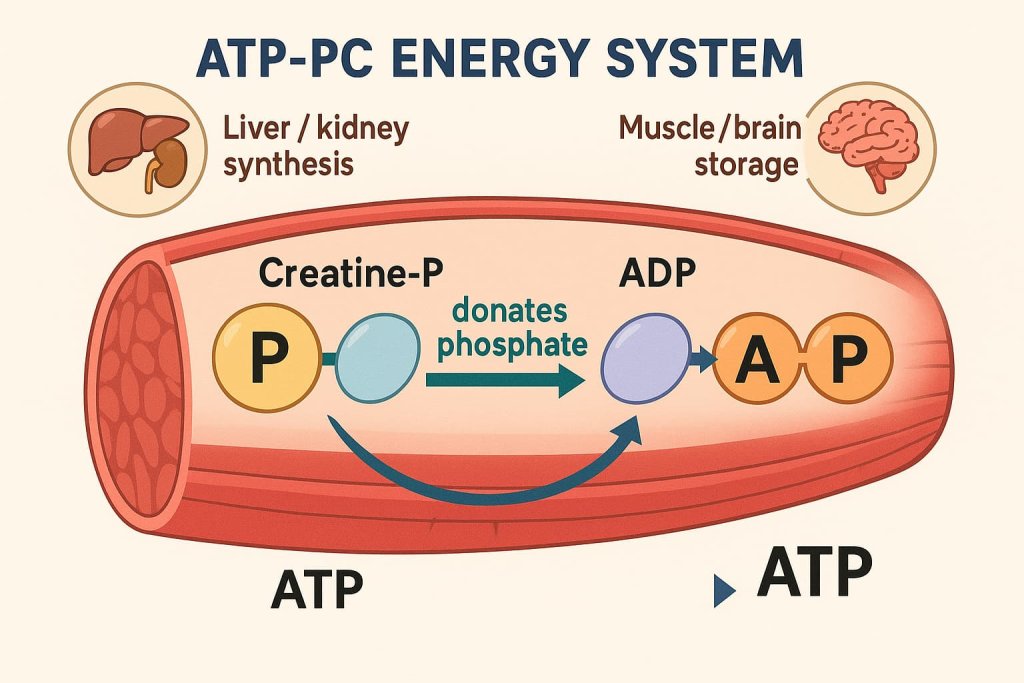
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound made from the amino acids arginine, glycine, and methionine. The human body produces about 1–2 grams of creatine daily, mainly in the liver and kidneys.
- About 95% of creatine is stored in skeletal muscles, where it plays a critical role in energy production.
- The rest is found in the brain, heart, and other tissues, where it supports high-demand energy activities (Mayo Clinic, 2024).
The Energy Cycle (ATP Regeneration)
Creatine’s main function is to regenerate adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the body’s primary energy molecule. During intense exercise or mental effort, ATP is rapidly depleted. Creatine helps recycle ATP faster, allowing for longer endurance, strength, and cognitive performance.
Dietary Sources
- Creatine is found in red meat, poultry, and fish.
- However, the average diet only provides about 1–2 g/day, which may not be enough to maximize muscle and brain stores.
- Vegetarians and vegans typically have lower baseline creatine levels, making supplementation especially beneficial (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024).
Physical Performance Benefits of Creatine

1. Increases Strength and Power
Creatine is the most effective supplement for strength and high-intensity performance.
- A meta-analysis shows creatine can increase muscle power and strength by 5–15%, depending on the exercise type (Mayo Clinic, 2024).
- This makes it highly effective for athletes in sprinting, weightlifting, and football.
2. Boosts Muscle Growth
- Creatine promotes muscle hypertrophy by drawing water into muscle cells, triggering protein synthesis.
- Studies show creatine supplementation combined with resistance training leads to greater muscle size gains compared to training alone (National Library of Medicine).
3. Improves Recovery Between Workouts
Creatine reduces exercise-induced muscle damage and helps restore glycogen faster.
- Athletes supplementing with creatine report less soreness and quicker recovery, enabling harder and more frequent training (Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 2017).
4. Reduces Injury Risk
By strengthening muscles and improving bone health, creatine lowers the risk of:
- Muscle strains
- Bone fractures
- Overuse injuries
This makes creatine especially valuable for athletes under heavy training loads.
Cognitive Benefits of Creatine You Didn’t Know

While creatine’s muscle benefits are well known, its brain benefits are just starting to gain attention.
1. Enhances Memory and Learning
A 2024 systematic review concluded that creatine supplementation improves:
- Short-term memory
- Attention span
- Information processing speed
This was particularly significant in vegetarians, vegans, and older adults (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024).
2. Protects Against Mental Fatigue
Creatine supports neuronal energy during demanding tasks, reducing mental fatigue. This makes it useful for:
- Students studying for exams
- Professionals with long working hours
- E-sports players and gamers needing sustained focus
3. Alzheimer’s and Brain Health
A 2025 University of Kansas Medical Center study found creatine supplementation increased brain creatine levels by 11% in Alzheimer’s patients. Participants also showed moderate improvements in memory and executive function (KUMC, 2025).
4. Neuroprotection
Animal and human studies suggest creatine may protect against:
- Parkinson’s disease progression
- Oxidative stress and neuron damage
- Cognitive decline in aging
This positions creatine as a potential therapeutic aid for neurodegenerative conditions.
Benefits of Creatine for Aging and Longevity

Creatine is just as important for seniors as it is for athletes.
1. Prevents Muscle Loss (Sarcopenia)
Sarcopenia—the gradual loss of muscle with age—is a major contributor to frailty.
- A 2019 study in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle found creatine supplementation, combined with resistance training, significantly improved muscle mass and strength in older adults (PubMed, 2019).
2. Supports Bone Health
- Creatine enhances bone density and may lower the risk of osteoporosis.
- Particularly important for post-menopausal women, who face accelerated bone loss (Woman & Home, 2024).
3. Improves Balance and Reduces Falls
Studies suggest creatine supplementation in seniors improves balance and neuromuscular control, reducing fall risk—a leading cause of disability in aging populations.
Dosage, Safety, and Best Practices
Recommended Dosage
- Standard maintenance: 3–5 grams daily.
- Loading phase (optional): 20 g/day (split into 4 doses) for 5–7 days, then 3–5 g/day.
- Works best when taken daily, consistently (Health.com, 2025).
Safety
- Decades of research confirm creatine is safe for long-term use in healthy individuals.
- No evidence links creatine to kidney or liver damage (Mayo Clinic, 2024).
- Common side effect: mild water retention in muscles, which is harmless.
Cost
- Creatine monohydrate is one of the most affordable supplements, averaging under $0.50 per serving (Business Insider, 2025).
Side Effects of Creatine: What Research Says

✅ Well-Researched Safety
Creatine is one of the most studied supplements in the world.
Long-term studies (up to 5 years) show no harmful effects on kidney, liver, or cardiovascular health in healthy individuals taking 3–5 g/day. (Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 2017)
⚠️ Possible Side Effects
1. Water Retention & Weight Gain
Creatine draws water into muscles, leading to a 0.5–1.5 kg increase in body weight during the first weeks.
This is not fat gain—it’s mostly intramuscular water. (PubMed Review)
2. Digestive Discomfort
Some users experience bloating, diarrhea, nausea, or cramps, especially with high doses or loading phases.
Splitting doses or taking with food usually prevents this. (WebMD on Creatine)
3. Muscle Cramps & Dehydration (Myth)
Early anecdotal reports suggested creatine may cause cramps, but controlled studies found no increased risk—in fact, some show it reduces cramping in athletes. (JISSN, 2017)
4. Kidney Function Concerns
Creatine can raise serum creatinine levels, a biomarker for kidney function.
This can be misinterpreted as kidney damage, but in healthy users, studies show no real harm. However, people with existing kidney disease should avoid creatine unless approved by a doctor. (Times of India – Kidney & Creatine)
5. Hair Loss (Unproven)
A small 2009 study suggested creatine might raise DHT (dihydrotestosterone), a hormone linked to hair loss.
No follow-up studies have confirmed this. Current consensus: no strong evidence creatine causes hair loss. (Health.com Report)
📌 Bottom Line
For healthy adults, creatine (3–5 g/day) is safe long-term.
The most common side effects are mild digestive upset and temporary water retention.
Those with pre-existing kidney issues should consult a doctor before using creatine.
🔗 Further Reading
- Should I be taking creatine? (FT.com)
- Kidneys and creatine: How to make sure the supplement doesn’t backfire (Times of India)
- Creatine benefits and drawbacks (The Guardian)
Common Myths About Creatine (Debunked)
- ❌ Creatine causes hair loss → No scientific evidence supports this claim (Health.com, 2025).
- ❌ You must cycle off creatine → Continuous use is safe.
- ❌ It damages the kidneys → Proven safe in healthy adults.
- ❌ Only for athletes → Benefits extend to students, women, and seniors.
Choosing the Best Creatine Supplement
When selecting a supplement, look for:
- Creatine Monohydrate (most studied and effective)
- Third-party testing for purity and safety
- Avoid “designer blends” with unnecessary fillers
Trusted supplement brands like Optimum Nutrition, Thorne, and Transparent Labs offer high-quality, lab-tested creatine.
FAQs About Creatine
1. Is creatine safe for long-term use?
Yes—research over 20 years confirms safety for healthy individuals (Mayo Clinic).
2. Can older adults benefit from creatine?
Yes—it preserves muscle mass, bone density, and cognitive health (PubMed, 2019).
3. Does creatine benefit vegetarians more?
Yes, because their baseline levels are lower, supplementation has a greater effect (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024).
4. Does creatine cause bloating?
No—creatine increases intramuscular water, not belly fat (Health.com, 2025).
5. Is creatine good for women?
Yes—it supports bone strength, hormone balance, and energy.
6. Should I take creatine before or after workouts?
Timing is flexible—daily consistency matters more than timing.
7. Can creatine improve workplace or study performance?
Yes, research shows improved memory and reduced fatigue in cognitive tasks (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024).
Conclusion
Creatine is not only the most effective supplement for athletes, but also one of the most versatile and affordable health enhancers. Backed by decades of research, it helps with:
- Strength and muscle growth
- Faster recovery and reduced injuries
- Improved memory, focus, and brain protection
- Prevention of age-related muscle and bone loss
If you want one supplement that supports body, brain, and aging—creatine is scientifically proven to deliver. As always, consult your healthcare provider before starting supplementation if you have medical conditions.
References
- Mayo Clinic – Creatine
- Frontiers in Nutrition – Systematic Review (2024)
- University of Kansas Medical Center – Alzheimer’s Pilot Study (2025)
- Journal of the ISSN – Creatine Safety (2017)
- Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle (2019)
- Health.com – Creatine Safety & Myths
- Business Insider – Rising Demand for Creatine (2025)
- Woman & Home – Dr. Amir Khan on Creatine
