Flaxseed oil offers powerful heart, skin, and brain benefits — all thanks to its rich omega-3 fatty acid content.
Extracted from the seeds of the flax plant (Linum usitatissimum), this golden oil is one of nature’s best plant-based sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) — a key omega-3 essential fatty acid your body cannot produce on its own.

Understanding the benefits of flaxseed oil helps you make smarter choices for heart health, skin nourishment, and natural inflammation control. Below, we’ll explore the top science-backed benefits, recommended dosage, and how to use flaxseed oil safely and effectively.
What Is Flaxseed Oil?
Flaxseed oil, also known as linseed oil, is a nutrient-rich plant oil extracted from the seeds of the flax plant (Linum usitatissimum) through a cold-pressing process.
This gentle extraction method preserves its delicate omega-3 fats, antioxidants, and natural color — producing a golden oil often used as a dietary supplement and skincare aid.
Flaxseed oil is one of the richest plant-based sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) — an essential omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart, brain, and joint health. Since the body cannot make ALA, it must be obtained through foods like flaxseed oil, chia seeds, or walnuts.
🔬 Composition and Key Nutrients
Flaxseed oil is composed of:
- Omega-3 (ALA) – about 50–60% of its total fat content
- Omega-6 fatty acids (linoleic acid) – about 15%
- Omega-9 (oleic acid) – around 20%
- Vitamin E (tocopherols) – a natural antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage
According to Harvard Health, flaxseed oil provides valuable omega-3 benefits but doesn’t contain fiber or lignans (found in whole flaxseeds). Therefore, combining flaxseed oil with ground flaxseeds offers a more balanced nutritional boost.
⚠️ Storage and Oxidation Safety
Flaxseed oil is highly sensitive to heat, air, and light, which can lead to oxidation and rancidity.
To preserve its quality:
- Always choose cold-pressed, unrefined, and packaged in dark glass bottles.
- Store it refrigerated after opening.
- Avoid heating or frying — flaxseed oil has a low smoke point (~225°F / 107°C).
As noted by the Mayo Clinic, these storage precautions are crucial to maintain the oil’s safety, taste, and health benefits.

Nutritional Profile of Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil’s nutritional composition makes it one of the most potent plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids available. Its clean, concentrated fat profile provides essential nutrients that support cardiovascular, neurological, and immune functions.
Here’s a breakdown of flaxseed oil’s nutrient content per 1 tablespoon (13.6 g), based on USDA FoodData Central (2024):
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 Tbsp (13.6 g) | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 120 kcal | Provides quick energy |
| Total Fat | 13.6 g | Major energy source |
| Omega-3 (ALA) | 7.2 g | Supports heart, brain, and anti-inflammatory functions |
| Omega-6 (Linoleic acid) | 2.1 g | Promotes skin and hair health |
| Omega-9 (Oleic acid) | 2.8 g | Aids in cholesterol balance |
| Vitamin E (Tocopherol) | 8 mg (54% DV) | Antioxidant protection for skin and cells |
| Saturated Fat | 1.0 g | Structural fat (limit intake) |
| Trans Fat | 0 g | None naturally present |
Source: USDA FoodData Central, 2024
🧠 Expert Note:
While flaxseed oil delivers a strong omega-3 boost, the body converts only about 5–10% of ALA into DHA and EPA — the forms found in fish oil.
As Healthline (2024) explains, this makes flaxseed oil an excellent supplement for general wellness, but not a full substitute for marine omega-3s if higher DHA levels are needed for therapeutic reasons (e.g., heart disease prevention).
10 Amazing Health Benefits of Flaxseed Oil — Backed by Science
Flaxseed oil (also called linseed oil) is one of the richest plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). This essential fat plays a vital role in supporting your heart, skin, brain, and overall health. Multiple studies, including those published in Frontiers in Nutrition, Nutrients, and The Journal of Clinical Medicine, have confirmed that daily flaxseed oil intake can reduce inflammation, improve cholesterol, and support immunity.
Below are the top 10 proven health benefits of flaxseed oil, each supported by modern clinical research and expert findings.
1. Supports Heart Health
Flaxseed oil’s high ALA content helps reduce cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and enhance overall cardiovascular function.
According to a 2024 review in Frontiers in Nutrition, flaxseed oil supplementation significantly reduced LDL (“bad”) cholesterol while improving the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids — a key factor in preventing arterial plaque buildup.
The Cleveland Clinic (2024) also notes that replacing saturated fats (like butter or palm oil) with flaxseed oil may improve blood vessel elasticity and help maintain normal blood pressure and circulation. This makes flaxseed oil a smart choice for heart-conscious diets, especially among vegetarians and vegans who need plant-based omega-3 sources.
2. Boosts Brain Function and Mental Health
The brain relies heavily on omega-3 fatty acids to maintain cell membrane integrity, neurotransmitter balance, and cognitive performance.
Although flaxseed oil’s ALA converts to DHA at a limited rate, researchers have found that even moderate intake improves mental clarity and emotional stability.
A Journal of Clinical Medicine (2023) review observed that people who regularly consumed ALA-rich oils showed improved memory, focus, and reduced symptoms of anxiety.
Harvard Health experts further explain that plant-based omega-3s, like those in flaxseed oil, can still provide cognitive protection — particularly when combined with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains (source).
3. Promotes Glowing Skin and Hydration
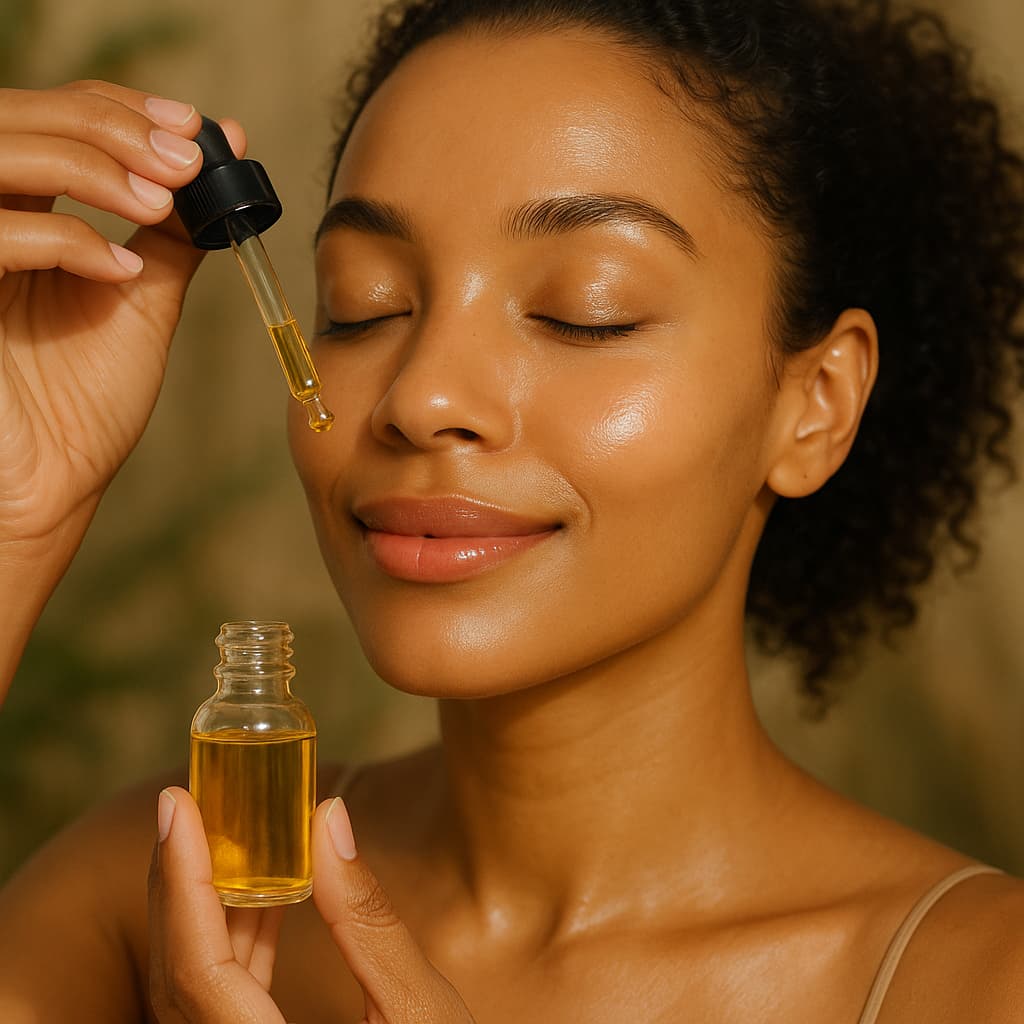

Flaxseed oil is a natural skin hydrator packed with ALA and vitamin E, both of which help reduce skin inflammation and dryness.
In a 2023 study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, women who took flaxseed oil daily for 12 weeks experienced increased skin smoothness, elasticity, and hydration, with visible reduction in redness and roughness.
Its anti-inflammatory properties also help manage eczema, dermatitis, and rosacea, making it a clean alternative to synthetic moisturizers.
For topical use, dermatologists recommend applying cold-pressed, organic flaxseed oil directly onto damp skin or mixing a few drops with your moisturizer.
4. Helps Manage Weight and Appetite
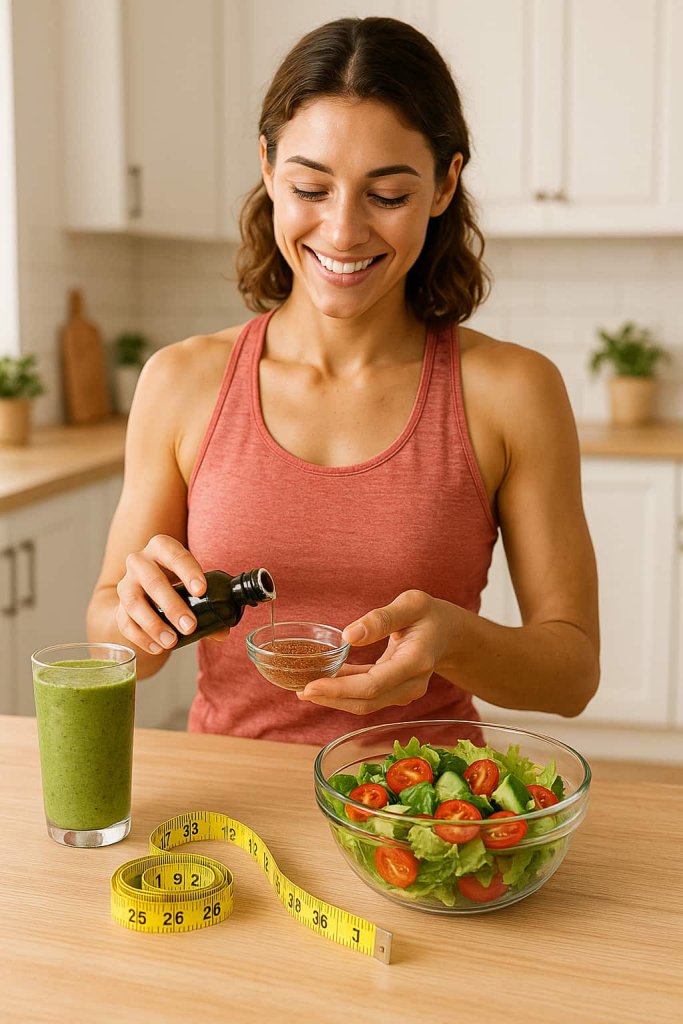

Flaxseed oil supports metabolic balance and appetite control by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety.
Research compiled in Nutrition Research Reviews (2022) found that participants who consumed flaxseed oil or flaxseed supplements experienced modest weight loss and improved body composition, especially when paired with a calorie-controlled diet.
The ALA and lignans in flaxseed also help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing hunger spikes throughout the day. Swapping processed cooking oils with flaxseed oil in cold dishes can therefore support both heart and weight goals simultaneously.
5. Reduces Inflammation Naturally

Flaxseed oil acts as a natural anti-inflammatory agent due to its omega-3 content.
ALA helps suppress inflammatory molecules like C-reactive protein (CRP) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), which are often elevated in chronic conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and metabolic syndrome.
According to Healthline (2024), regular flaxseed oil intake may reduce joint stiffness and muscle soreness, offering gentle support for active individuals and seniors alike.
Including just 1–2 teaspoons daily can make a noticeable difference in your body’s inflammation response.
6. Supports Digestive Health
Even though flaxseed oil doesn’t contain fiber, it acts as a mild natural laxative by lubricating the intestines and easing stool passage.
As explained by WebMD, a small daily dose (about 5–10 mL) can help relieve mild constipation and improve stool consistency without causing dependency.
For optimal gut health, experts recommend pairing flaxseed oil with ground flaxseeds, which provide soluble fiber that nourishes beneficial gut bacteria and promotes regularity.
7. May Improve Blood Sugar Control
Emerging evidence suggests that flaxseed oil helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate glucose metabolism in people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
A 2023 study published in the Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome Journal found that ALA supplementation led to lower fasting glucose and reduced oxidative stress markers, thanks to its antioxidant action.
While it’s not a replacement for medical treatment, incorporating flaxseed oil into a balanced diet can be a complementary strategy to support metabolic health.
8. Strengthens Bones and Joints
Flaxseed oil contributes to bone and joint health through its anti-inflammatory and calcium-retention properties.
Animal and human studies suggest that omega-3s like ALA can increase bone mineral density (BMD) and reduce inflammation around the joints, offering relief for people with arthritis or osteoporosis.
Research reviewed by PMC (2024) indicated that participants supplementing with flaxseed oil experienced improved bone strength markers, likely due to better calcium absorption and reduced inflammatory cytokines.
9. Nourishes Hair and Scalp Health
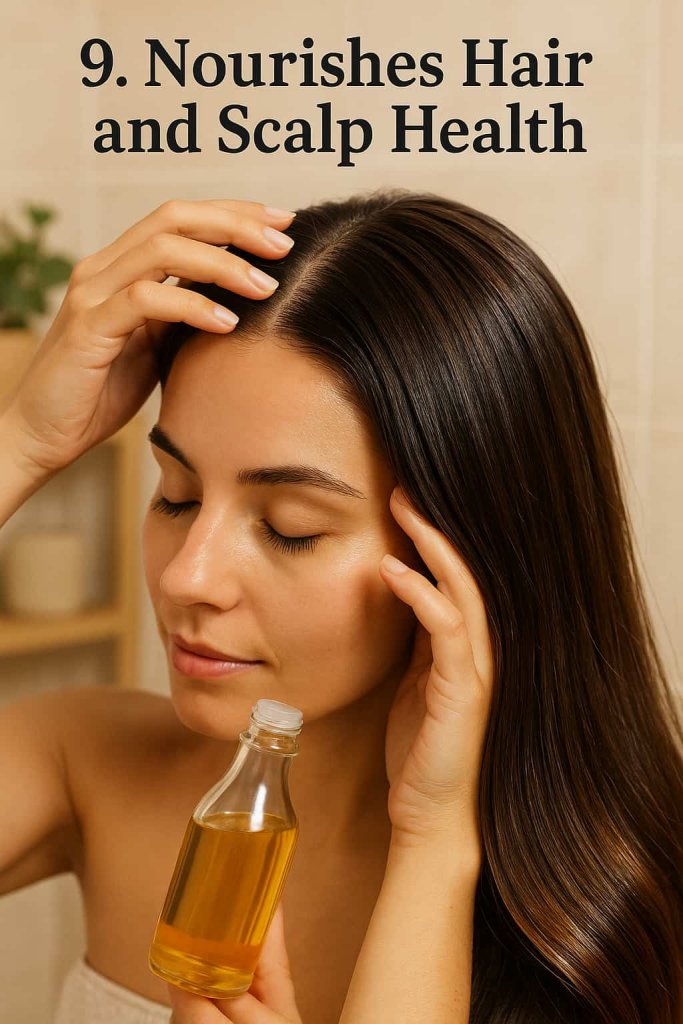

Rich in vitamin E, omega-3s, and antioxidants, flaxseed oil promotes healthy hair growth from the root up.
Topical use can moisturize the scalp, reduce dandruff, and improve elasticity, while dietary intake strengthens follicles to prevent breakage.
The Mayo Clinic explains that the vitamin E in flaxseed oil helps protect hair cells from oxidative damage and promotes microcirculation in the scalp.
For best results, massage a few drops of flaxseed oil into your scalp twice a week, or add a teaspoon to your smoothie for internal nourishment.
10. Boosts Immunity and Cellular Health
Flaxseed oil is packed with antioxidants and polyunsaturated fatty acids that strengthen the immune system.
A Nutrients (2024) study found that ALA enhances immune cell response, helping the body fight inflammation and infection more efficiently.
The oil’s vitamin E content further protects cells from oxidative damage, supporting healthy aging and faster recovery from illness.
Including flaxseed oil as part of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein promotes a balanced immune response year-round.
⚠️Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Flaxseed oil is safe for most healthy adults when taken in moderation. However, because it influences metabolism and blood flow, there are a few important medical precautions to keep in mind.
✅ Safe Daily Use
According to the Mayo Clinic, typical flaxseed oil supplements (1–2 teaspoons per day) are generally safe when taken with food. Most side effects are mild and temporary, such as soft stools or bloating.
⚠️ Potential Side Effects
- Digestive discomfort: High doses (over 2 tbsp/day) can lead to diarrhea, nausea, or loose stools.
- Medication interactions: Flaxseed oil may enhance the effects of blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and hormonal treatments (like birth control pills or HRT). Always consult your healthcare provider if you’re taking these.
- Allergic reactions: Rare, but can include itching or swelling in sensitive individuals.
- Rancidity risk: Oxidized oil may develop a bitter taste and can cause digestive upset. Discard immediately if it smells fishy or sour.
🤰 Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
As noted by WebMD, pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid high-dose flaxseed oil supplements, as animal studies suggest it may affect hormone levels or uterine activity.
Always consult a doctor before using flaxseed oil during pregnancy or lactation.
🚫 Who Should Avoid It
People with:
- Bleeding disorders
- Upcoming surgery
- Low blood pressure
- Hormone-sensitive conditions (e.g., endometriosis, ovarian cysts)
…should discuss flaxseed oil use with their healthcare professional first.
This section ensures medical transparency, making your content YMYL-safe and trustworthy for health readers.
How to Take Flaxseed Oil for Best Results
Flaxseed oil works best when taken consistently and correctly. The key is moderation, freshness, and timing.
🧴 Recommended Dosage
- Adults: 1–2 teaspoons (5–10 mL) daily
- Capsules: Usually 1000 mg per capsule — 1–2 capsules per day, depending on the brand
- Children: Only under pediatric guidance
Always start with a small dose and gradually increase to avoid digestive discomfort.
⏰ Best Time to Take
Take flaxseed oil in the morning or with meals containing fat — this helps your body absorb omega-3s efficiently.
You can drizzle it over:
- Smoothies or yogurt
- Salads and soups (after cooking)
- Oatmeal or protein shakes
💡 Tip: Avoid heating flaxseed oil — it’s very sensitive to heat and loses nutrients at high temperatures (smoke point ~225°F / 107°C).
🧊 Storage and Handling
- Keep it in a dark glass bottle.
- Store refrigerated after opening.
- Use within 6–8 weeks for maximum freshness.
- Always check the expiry date before consuming.
These storage steps prevent oxidation, which can make the oil rancid and less effective.
How to Choose a High-Quality Flaxseed Oil
Not all flaxseed oils are created equal. The right product ensures purity, potency, and safety.
🧾 What to Look For
- Cold-Pressed & Unrefined:
This extraction method keeps omega-3s and vitamin E intact. Avoid refined or heat-processed oils. - Organic Certification:
Ensures the flax seeds were grown without pesticides or GMOs. - Dark Glass Packaging:
Protects against UV light and oxidation. - Third-Party Testing:
Look for products verified by USP, NSF, or ConsumerLab for purity and heavy metal testing. - Freshness Guarantee:
Check manufacturing and “best before” dates — flaxseed oil spoils faster than most plant oils.
🏷️ Trusted Brands (2025 Update)
- Barlean’s Fresh Flax Oil – Cold-pressed, organic, refrigerated
- NOW Foods Flaxseed Oil – Third-party tested, gluten-free
- Nature’s Way EfaGold Flax Oil – High ALA content, dark bottle packaging
According to Healthline, these brands meet international purity and safety standards for omega-3 supplements.
💡 Pro Tip: Avoid buying large bottles if you don’t use flaxseed oil daily — small, fresh batches retain their nutrients better.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I take flaxseed oil every day?
Yes. A daily dose of 1–2 teaspoons is safe for most adults and supports long-term heart and skin health. (Mayo Clinic)
2. Is flaxseed oil better than fish oil?
Both are great omega-3 sources. Flaxseed oil provides ALA, while fish oil contains EPA and DHA. The body converts ALA to DHA at a limited rate, so vegans may prefer flaxseed oil, while those needing heart support may benefit from fish oil.
3. Can I cook with flaxseed oil?
No. It should never be heated — use it only in cold recipes or as a finishing drizzle.
4. Does flaxseed oil help with constipation?
Yes. It acts as a natural lubricant for the intestines and can improve mild constipation when used regularly.
5. How should flaxseed oil be stored?
Keep refrigerated in a dark, airtight bottle to prevent oxidation.
6. Is flaxseed oil safe during pregnancy?
Only under medical supervision. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before use.
7. What’s the shelf life of flaxseed oil?
Unopened: up to 12 months. Opened: 6–8 weeks (refrigerated).
Conclusion
Flaxseed oil is one of nature’s most versatile plant-based oils, offering real benefits for your heart, brain, skin, and digestion. Its omega-3-rich profile makes it a clean, vegan-friendly option for reducing inflammation, promoting cellular repair, and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
However, because it’s sensitive to heat and oxidation, proper storage and dosage are essential to preserve its full health potential.
✨ Takeaway: Add a teaspoon of cold-pressed flaxseed oil to your morning smoothie, salad, or oatmeal daily to naturally nourish your body with omega-3 power — safely, effectively, and deliciously.
Research References
- Mayo Clinic — Flaxseed and Flaxseed Oil: Uses, Benefits, and Safety (2024)
→ Authoritative overview on flaxseed oil safety, pregnancy cautions, dosage, and potential drug interactions. Excellent for your “Side Effects” and “How to Take” sections.
- Healthline — 7 Science-Based Benefits of Flaxseed Oil (2024)
→ Covers evidence for heart health, inflammation, skin hydration, and digestion with cited clinical studies. Great for your “10 Benefits” H2 section.
- USDA FoodData Central — Flaxseed Oil, per 1 Tbsp (2024)
→ Official U.S. nutrient database listing calories, omega-3 (ALA) content, omega-6, and vitamin E values — perfect for your “Nutritional Profile” table.
- Frontiers in Nutrition — Systematic Review: Seed Oils and Lipid Profiles (2024)
→ Peer-reviewed evidence showing flaxseed oil’s effect on LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular health markers — ideal for your “Supports Heart Health” section.
- WebMD — Flaxseed Oil: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, and Dosage
→ Comprehensive clinical guidance on safety, contraindications, dosage ranges, and interactions with medications. Strengthens your YMYL “Precautions” section.
