Sardines are among the healthiest fish you can eat — rich in omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and essential nutrients that protect your heart, bones, and brain. Packed with vitamins B12 and D, calcium, and selenium, sardines provide a powerful nutritional boost at a low cost. Understanding their health benefits helps you make smarter choices for long-term wellness and sustainable nutrition.

What Are Sardines? (Overview and Nutrition Facts)
Sardines are small, oily fish belonging to the herring family (Clupeidae), commonly found in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Mediterranean seas. They’re named after the Italian island of Sardinia, where they were once found in abundance.
These nutrient-dense fish are typically consumed fresh, grilled, smoked, or canned in water, olive oil, or tomato sauce. Because they feed on plankton and have a short life cycle, sardines accumulate very little mercury — making them one of the safest and most sustainable seafood choices, especially for children and pregnant women.
(FDA – Advice About Eating Fish, 2024)
Nutritional Profile of Sardines (Per 100 g, canned in oil, drained)
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 208 kcal | — |
| Protein | 24 g | 48% |
| Total Fat | 11 g | — |
| Omega-3 (EPA + DHA) | ≈ 1.5 g | — |
| Calcium | 382 mg | 38% |
| Vitamin D | 270 IU | 68% |
| Vitamin B12 | 8.9 µg | 370% |
| Selenium | 52 µg | 95% |
| Phosphorus | 490 mg | 35% |
| Iron | 2.9 mg | 16% |
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) FoodData Central, 2025
Why Sardines Are a Nutrient Powerhouse
- Complete protein: Contains all essential amino acids for muscle repair and metabolism.
- Heart-healthy omega-3s: EPA and DHA lower inflammation and support cardiovascular function.
- Bone-support nutrients: Calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D promote strong bones and teeth.
- Energy & brain health: High in vitamin B12 and selenium for red-blood-cell formation and antioxidant defense.
- Low mercury: Listed by the U.S. FDA as a Best Choice seafood for all age groups due to its minimal mercury content.
- Eco-friendly: Sardines reproduce quickly and are fished sustainably, making them an environmentally responsible source of marine nutrition.
10 Proven Health Benefits of Sardines (Science-Based)
1. Promotes Heart Health
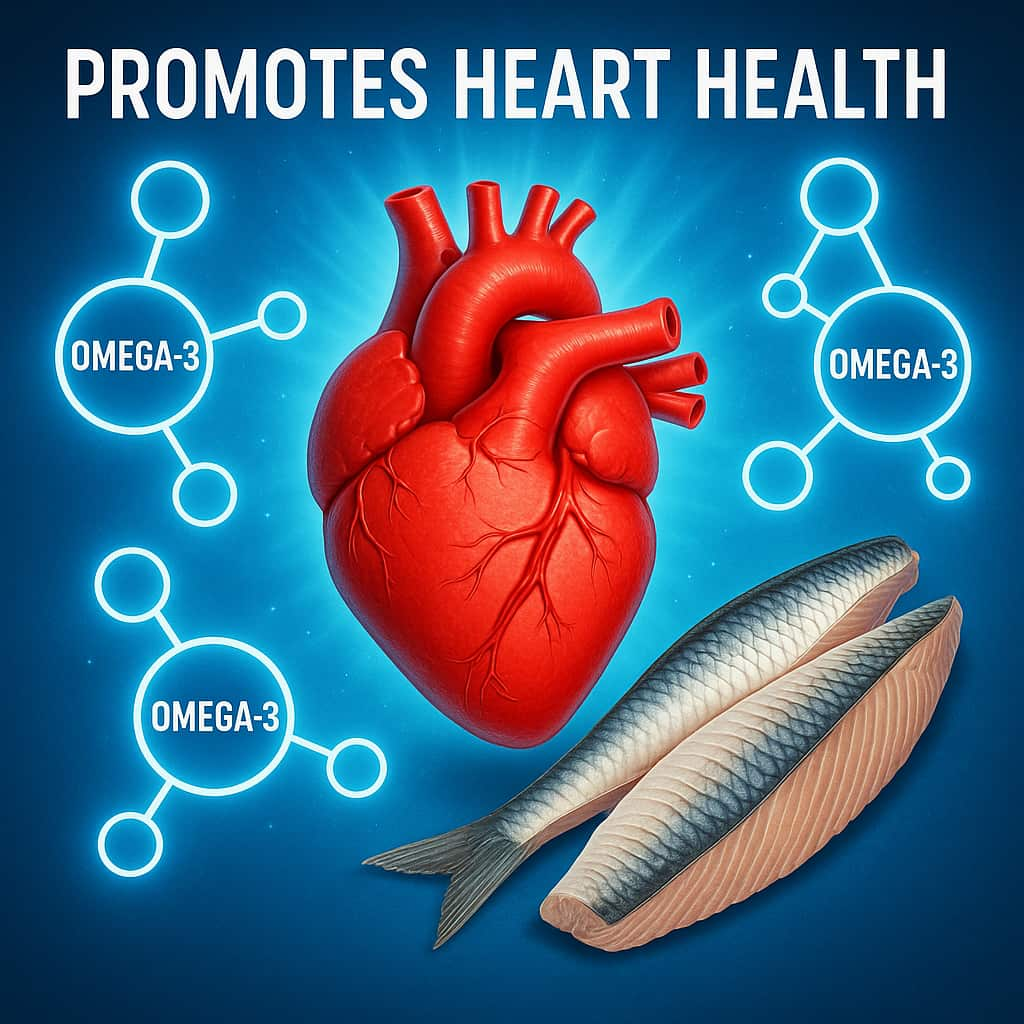
Sardines are one of the richest natural sources of omega-3 fatty acids — specifically EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) — both proven to support cardiovascular function. These healthy fats reduce triglyceride levels, improve blood vessel elasticity, and help stabilize heart rhythm.
A 2021 meta-analysis in Frontiers in Nutrition found that people who regularly consumed oily fish had a 20–25% lower risk of cardiovascular mortality compared to those who did not.
According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, omega-3 fats reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and prevent blood clots — all key for heart protection.
Takeaway: Including sardines twice a week provides the heart-protective benefits of fish oil in a natural, nutrient-dense form.
2. Strengthens Bones and Teeth
Sardines are uniquely rich in calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus, which are crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH, 2024) confirms that vitamin D enhances calcium absorption and bone mineralization, while phosphorus and protein provide the structural foundation of bone tissue.
A 100-gram serving of canned sardines with bones offers nearly 40% of your daily calcium needs and over 60% of your vitamin D intake, according to NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
Takeaway: Regularly consuming sardines — especially with edible bones — can naturally prevent osteoporosis and maintain dental strength as you age.
3. Supports Brain Health and Cognitive Function

The brain is composed of about 60% fat, and DHA — found abundantly in sardines — is essential for brain cell structure and communication.
A 2022 study in Nutrients showed that adults with higher omega-3 intake experienced better memory, focus, and slower cognitive decline.
Moreover, sardines provide vitamin B12, which supports neurotransmitter synthesis and reduces the risk of cognitive impairment.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, omega-3s enhance blood flow to the brain and may protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Takeaway: Regular sardine consumption supports lifelong brain health, improved mood, and mental sharpness.
4. Aids in Weight Management

Sardines are naturally high in lean protein and heart-healthy omega-3 fats, both of which promote satiety and help regulate appetite.
A single 3.75-ounce can provides about 22 grams of complete protein, supporting muscle repair, metabolism, and hormonal balance that control hunger signals.
According to Harvard Health Publishing – How much protein do you need every day?, protein helps preserve lean body mass, increases metabolic rate, and supports weight maintenance when paired with regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
Practical Tip: Enjoy sardines on whole-grain toast, toss them into a quinoa or leafy-green salad, or mix them into brown rice with vegetables.
These balanced meals combine fiber, healthy fats, and protein — keeping you full and energized longer than processed snacks.
5. Reduces Inflammation and Improves Immunity
Chronic inflammation contributes to conditions like arthritis, asthma, and heart disease — and sardines can help fight it naturally.
They contain omega-3s (EPA and DHA) and selenium, which reduce inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, improving immune response and reducing oxidative stress.
A 2023 review in Marine Drugs concluded that fish-derived omega-3s can suppress chronic inflammation and enhance immune defense.
Selenium, an essential mineral found in sardines, acts as an antioxidant cofactor that strengthens immune cell activity (NIH Selenium Fact Sheet).
Takeaway: Eating sardines 2–3 times per week helps calm inflammation and supports a stronger immune system.
6. Supports Healthy Skin and Hair

The omega-3 fatty acids in sardines nourish the skin from the inside out by reinforcing its lipid barrier, which keeps it hydrated, elastic, and resistant to irritation. These fats also help reduce inflammation that can lead to redness, dryness, and premature aging.
Sardines are rich in vitamin B12 and protein, both vital for cell regeneration and strong, healthy hair. Vitamin B12 aids red blood cell formation — improving oxygen delivery to skin and scalp — while protein provides the amino acids necessary for keratin production. In addition, selenium, an antioxidant mineral in sardines, protects skin cells from oxidative stress and UV damage.
According to the Cleveland Clinic – 23 Foods To Eat for Healthier Skin, fatty fish like sardines supply essential omega-3s and antioxidants that support skin smoothness, moisture retention, and overall glow.
Takeaway: Regularly including sardines in your diet helps promote radiant skin and stronger hair, making them one of nature’s most effective “beauty-from-within” foods.
7. Helps Manage Blood Sugar and Insulin Sensitivity
Sardines can be particularly helpful for individuals managing or at risk for type 2 diabetes.
A 2021 clinical trial in Lipids in Health and Disease reported that adults with prediabetes who consumed sardines twice a week for six months had better insulin sensitivity and lower HbA1c compared with a control group.
Researchers attribute this benefit to the combined effects of omega-3 fatty acids, taurine, and calcium, which help improve glucose metabolism and reduce chronic inflammation.
Omega-3s also enhance the flexibility of cell membranes, allowing insulin to work more effectively.
According to the Cleveland Clinic – Why Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Good for You, omega-3s improve heart and metabolic health by lowering inflammation and supporting more efficient cellular function.
Takeaway: Combine sardines with fiber-rich foods—like lentils, leafy greens, or quinoa—to stabilize blood sugar naturally and support long-term metabolic balance.
8. Boosts Mood and Mental Health

Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to support mental and emotional health by influencing neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, reducing brain inflammation, and improving communication between nerve cells.
A 2022 systematic review in Translational Psychiatry found that supplementation with EPA and DHA, the main omega-3s in sardines, significantly improved mood stability and reduced depressive symptoms in adults.
Because sardines naturally contain both omega-3s and vitamin B12, they help maintain neurotransmitter balance—a key factor in reducing anxiety, depression risk, and cognitive decline.
According to the Cleveland Clinic – Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Why They’re Good for Your Health, omega-3s contribute to healthy brain function, lower stress-related inflammation, and may help protect against mood disorders.
Takeaway: Sardines are a natural “mood-lifting” food — providing the omega-3s and vitamin B12 that support sharper focus, calmer mood, and better emotional resilience.
9. Supports Eye Health and Vision

DHA, a structural fat found in the retina, is vital for visual development and eye function.
The American Optometric Association (AOA) reports that omega-3s help reduce symptoms of dry eye syndrome and may lower the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). (AOA Omega-3 Guidelines)
Sardines, being one of the richest sources of DHA, support clear vision and long-term eye health when eaten regularly.
Takeaway: Add sardines to your diet to protect your eyes naturally and keep your vision sharp as you age.
10. Enhances Longevity and Overall Health

Sardines provide a rare combination of omega-3s, calcium, vitamin D, selenium, and antioxidants, which work together to protect cells from oxidative damage — a key factor in aging and chronic disease.
A 2023 Harvard Public Health study found that individuals who ate oily fish 2–3 times per week had a 13% lower risk of all-cause mortality compared to those who rarely ate fish.
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health emphasizes that omega-3-rich fish promote cardiovascular, brain, and overall longevity benefits.
Takeaway: Regular sardine intake is a simple, affordable, and science-backed way to live longer and stay healthier.
How to Eat Sardines for Best Results

Knowing how to eat sardines safely and effectively ensures you get their full nutritional benefits while minimizing risks. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), adults should aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week, such as sardines, to support optimal heart health.
Ideal Serving Frequency
- 2–3 servings per week (about 3–4 oz or one small can per serving).
- Provides enough omega-3s (EPA + DHA) to support cardiovascular, brain, and immune function.
- Rotate with other low-mercury fish (like salmon or trout) for dietary variety.
Best Preparation Methods
- Grilled or baked sardines preserve nutrients and reduce excess fat.
- Canned sardines in olive oil or water are convenient and nutritious.
- Avoid deep-fried or heavily salted varieties that add unnecessary calories and sodium.
- Enhance flavor naturally with lemon juice, herbs (parsley, dill), garlic, or olive oil.
Safe Storage and Handling
- Keep unopened cans in a cool, dry place.
- After opening, refrigerate leftovers in glass containers and consume within 1–2 days.
- If buying fresh sardines, store on ice and cook within 24 hours to maintain freshness.
Best Food Pairings
Pair sardines with:
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, arugula)
- Vitamin-C rich vegetables (tomatoes, bell peppers) — boosts iron absorption
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil) for better omega-3 uptake
Avoid High-Sodium or Processed Options
- Some canned sardines contain over 300 mg of sodium per serving.
- Choose “low sodium” or “in water/olive oil” options.
- Rinse canned sardines lightly before eating to reduce salt.
Pro Tip: Combine sardines with fresh lemon and olive oil for a Mediterranean-style meal — heart-healthy, flavorful, and nutrient-balanced.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions (Safety & Compliance Section)

While sardines are among the safest and most nutritious fish, certain health conditions call for moderation and awareness.
1. Sodium Caution
Canned sardines can be high in sodium (up to 400 mg per 3-ounce serving).
People with hypertension or kidney disease should choose low-sodium varieties or rinse canned sardines before eating.
(American Heart Association – Sodium Guidelines)
2. Purine Content (Gout Considerations)
Sardines naturally contain purines, compounds that can raise uric acid levels.
Individuals with gout or hyperuricemia should limit sardine intake to avoid triggering flare-ups.
(Arthritis Foundation – High-Purine Foods and Gout)
3. Seafood Allergies
Those with fish or shellfish allergies should avoid sardines entirely. Even trace amounts can cause reactions such as hives, swelling, or respiratory issues.
(Mayo Clinic – Fish Allergy Overview)
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Safety
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies sardines as a “Best Choice” seafood because of their low mercury levels and high nutrient value.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women can safely eat 2–3 servings (8–12 oz) per week of sardines.
(FDA – Advice About Eating Fish (2024))
Bottom Line: Sardines are safe for most people when eaten in moderation, but individuals with gout, allergies, or high blood pressure should practice portion control or consult a healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I eat sardines every day?
Yes, but it’s best to limit to 2–3 servings weekly to balance omega-3 intake and sodium consumption.
2. Are sardines better than fish oil supplements?
Yes. Sardines provide whole-food nutrients like protein, calcium, and selenium, which fish oil supplements lack.
3. Do sardines have mercury?
Sardines are very low in mercury due to their small size and short lifespan.
They are listed as a “Best Choice” in the FDA seafood safety chart.
4. Are sardines good for cholesterol?
Yes. Omega-3s in sardines raise HDL (good cholesterol) and lower triglycerides, improving heart health.
5. Are fresh or canned sardines healthier?
Both are nutritious. Fresh sardines retain slightly more omega-3s, while canned versions provide calcium from edible bones and year-round convenience.
6. Can sardines help with joint pain or arthritis?
Yes. The anti-inflammatory omega-3s in sardines help reduce stiffness and joint pain associated with arthritis.
7. What’s the best time to eat sardines?
Anytime — but many people enjoy them at lunch or dinner for a satisfying, high-protein meal that supports sustained energy.
Conclusion
Sardines are a nutritional powerhouse in a tiny package — rich in omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, vitamin D, and antioxidants that promote heart, brain, and bone health.
They’re affordable, sustainable, and low in mercury, making them a top choice for anyone seeking balanced nutrition and long-term wellness.
Adding sardines to your weekly menu 2–3 times per week can help lower inflammation, improve cholesterol, and support healthy aging — all backed by modern nutrition science.
References
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – Omega-3 Fats
Comprehensive overview of EPA and DHA roles in heart, brain, and metabolic health. - American Heart Association – Fish and Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Official guidance on serving frequency, omega-3 benefits, and heart-protective dietary habits. - National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Vitamin D Fact Sheet
Scientific summary of vitamin D’s role in calcium absorption and bone health. - U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – Advice About Eating Fish (2024)
Current federal safety chart for mercury levels and seafood consumption during pregnancy.
