Dark chocolate is more than a treat—it’s a nutrient-rich superfood with proven benefits for your heart, brain, and overall wellness. Studies show that cocoa flavanols, antioxidants, and minerals in high-quality dark chocolate may support circulation, mood balance, and healthy aging when consumed in moderation.

Understanding how to choose the right type, control portions, and recognize potential side effects ensures you enjoy dark chocolate safely as part of a balanced diet. This guide explains the 10 proven health benefits of dark chocolate, how it supports well-being, and how to select the best varieties based on scientific evidence and expert recommendations.
What Is Dark Chocolate? (Overview and Nutrition Profile)
Dark chocolate is a type of chocolate made primarily from cocoa solids, cocoa butter, and a small amount of sugar. Unlike milk chocolate, it contains little to no milk solids and typically features a cocoa content of 70% or higher, which gives it a rich, slightly bitter flavor and a higher concentration of beneficial plant compounds known as flavanols.
The health potential of dark chocolate comes mainly from its cocoa content, which is derived from fermented and roasted cacao beans (Theobroma cacao). These beans are naturally rich in antioxidants, magnesium, and iron, making dark chocolate one of the most nutrient-dense treats when consumed in moderation.
According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, dark chocolate’s high concentration of flavonoids may support heart, brain, and metabolic health by improving blood flow and reducing oxidative stress. However, the benefits depend greatly on the cocoa percentage and sugar levels—so higher-cocoa, lower-sugar varieties are best.
Nutrition Profile (Per 1 oz / 28 g of 70–85% Dark Chocolate)
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value (DV) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 170 | — |
| Total Fat | 12 g | 15 % |
| Saturated Fat | 7 g | 35 % |
| Carbohydrates | 13 g | 5 % |
| Fiber | 3 g | 11 % |
| Protein | 2 g | — |
| Iron | 3.4 mg | 19 % |
| Magnesium | 64 mg | 16 % |
| Copper | 0.5 mg | 25 % |
| Manganese | 0.7 mg | 30 % |
Source: USDA FoodData Central – Dark Chocolate, 70–85% Cocoa Solids
10 Proven Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate (Backed by Science)
Dark chocolate is more than a dessert—it’s a nutrient-dense superfood packed with flavanols, polyphenols, and essential minerals that support multiple aspects of wellness. Below are ten science-backed health benefits of dark chocolate, supported by recent clinical studies and nutrition research.
1. Supports Heart and Circulatory Health
Dark chocolate is rich in flavanols, compounds that support blood vessel flexibility, circulation, and nitric oxide production, all vital for cardiovascular function.
A 2025 Scientific Reports study found that daily consumption of cocoa flavan-3-ols helped lower systolic blood pressure and improve arterial elasticity, especially in adults with mild hypertension.
The Cleveland Clinic confirms that moderate dark chocolate intake—around one ounce daily—may support long-term heart health by maintaining healthy blood flow and reducing oxidative stress in arteries.
2. Provides Powerful Antioxidant Protection

Dark chocolate is among the most antioxidant-rich foods, even surpassing superfruits like blueberries and acai in overall antioxidant capacity. Its primary compounds—cocoa flavanols and polyphenols—play a vital role in neutralizing free radicals and supporting the body’s natural defense against oxidative stress.
According to a review published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry and supported by findings from PubMed Central, cocoa’s flavonoids help reduce oxidative damage to lipids and DNA, which may contribute to healthy aging and cellular protection.
Furthermore, a 2024 study in Food Research International reported that cocoa powder and dark chocolate may improve systemic oxidative status and reduce inflammation in adults when consumed in moderation.
(Source: ScienceDirect – Effects of Cocoa and Dark Chocolate on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation)
To maximize antioxidant benefits, nutrition experts recommend choosing dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa content, minimal added sugar, and ethically sourced ingredients. For additional insights, see Medical News Today – Dark Chocolate: Benefits, Nutrition, and Risks.
3. May Help Improve Brain Function and Focus
Flavanols in dark chocolate support cognitive performance by increasing blood flow to the brain and improving neural signaling.
A 2024 study from Georgia State University’s Lewis College found that consuming dark chocolate improved mental energy, focus, and fatigue recovery.
In addition, natural stimulants like caffeine and theobromine may promote alertness and help sustain concentration during mentally demanding tasks.
4. Supports Healthy Blood Sugar and Insulin Sensitivity

Regular intake of dark chocolate rich in cocoa flavonoids may help the body maintain balanced insulin sensitivity and glucose control.
According to the Diabetes Research & Wellness Foundation (DRWF), a long-term cohort study found that people who ate dark chocolate five or more times weekly had a 21 % lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared with non-consumers.
Choosing unsweetened or low-sugar chocolate helps optimize these potential metabolic benefits.
5. Promotes a Balanced Mood

Dark chocolate may naturally support emotional well-being thanks to its combination of mood-enhancing compounds and brain-protective antioxidants. It contains tryptophan, a building block for serotonin—the neurotransmitter that helps maintain a calm and balanced mood—and phenylethylamine (PEA), a natural compound that may promote energy and focus.
According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, cocoa flavanols found in dark chocolate may help support mood regulation and cognitive performance when enjoyed in moderation. These compounds appear to influence the brain through improved blood flow and protection against oxidative stress.
Further evidence from a Georgia State University study found that consuming 85% cocoa dark chocolate daily for three weeks was linked to lower negative mood scores and beneficial changes in gut bacteria, suggesting that cocoa polyphenols may positively impact the gut–brain axis.
Together, these findings highlight how moderate portions of quality dark chocolate (around 1 oz / 28 g per day) may support mental relaxation, stress resilience, and emotional balance—making it a scientifically supported comfort food when part of a healthy lifestyle.
6. Supports Gut and Microbiome Health
Emerging evidence shows that cocoa polyphenols can act as prebiotics, selectively nourishing beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
A 2025 Frontiers in Nutrition study reported that daily consumption of 85 % dark chocolate improved microbial diversity and gut barrier integrity, both linked to digestive and immune health.
This suggests dark chocolate may support the gut-brain axis, contributing to better mood and metabolism.
7. May Enhance Skin Health and Circulation

Dark chocolate’s potent antioxidants and flavanols support skin microcirculation and moisture retention.
A Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology (2024) trial found that participants who consumed cocoa daily for 12 weeks experienced improved skin hydration, texture, and UV resistance.
These effects are likely due to enhanced blood flow to the skin, aiding nutrient and oxygen delivery.
Learn more from Geisinger Health – Benefits of Dark Chocolate.
8. Supports Metabolic and Weight Balance

Although calorie-dense, dark chocolate contains fiber and healthy fats that can help control appetite and promote satiety.
A study published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024) found that adding small amounts of dark chocolate to meals reduced sugar cravings and prevented overeating.
To maintain energy balance, select chocolate with at least 70 % cocoa and minimal added sugar.
9. Contributes to Nutrient Intake

Dark chocolate is a source of iron, magnesium, copper, and zinc, which are crucial for blood formation, nervous system health, and immune defense.
These minerals support everyday functions like oxygen transport and energy metabolism.
Including modest portions can be especially beneficial for people with plant-based diets.
For nutrient details, visit Healthline – Dark Chocolate Nutrition.
10. May Support Longevity and Disease Prevention
A large 10-year cohort study reported by ScienceDaily (2025) showed that diets rich in flavonoid-containing foods—such as dark chocolate, berries, and tea—were linked to 16 % lower all-cause mortality and 10 % reduced risk of chronic diseases.
These benefits likely stem from the combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of diverse plant compounds, including cocoa flavanols.
For best results, combine dark chocolate with other nutrient-rich foods as part of a balanced diet.
How to Choose the Best Dark Chocolate
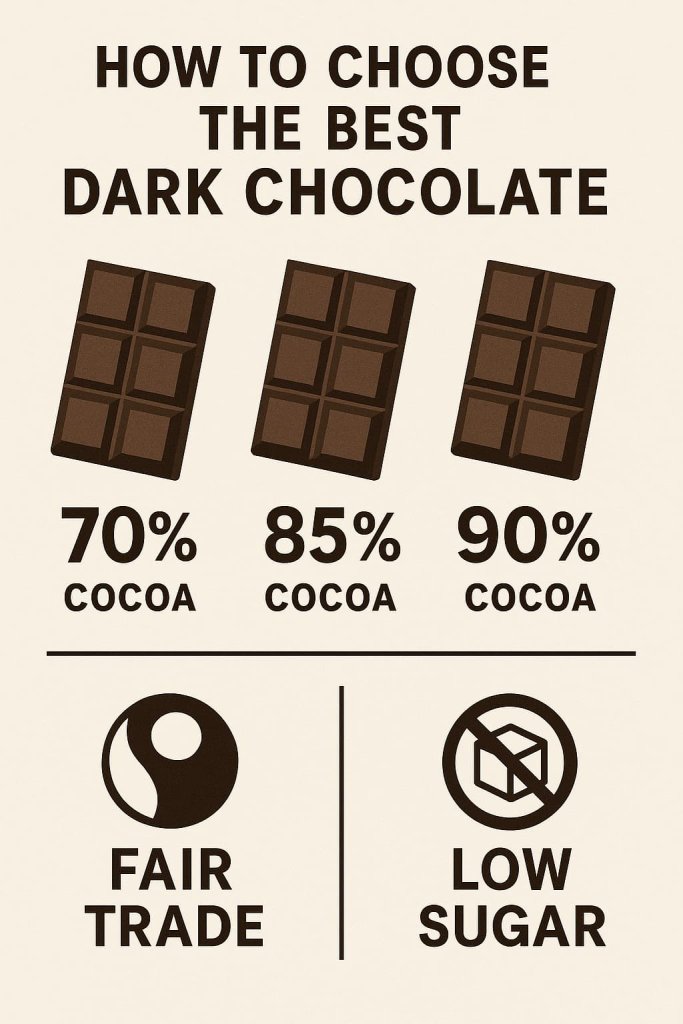
Selecting the right dark chocolate is essential to gain its health benefits without unnecessary additives or contaminants. The key is to focus on cocoa quality, sugar level, and purity rather than marketing claims.
1. Check the Cocoa Percentage
Choose bars with at least 70% cocoa solids. Higher cocoa content means greater flavanol concentration and fewer added sugars. According to the Cleveland Clinic, this range offers optimal antioxidant and heart-supporting benefits.
2. Read Ingredient Labels Carefully
Look for simple ingredients like cocoa mass, cocoa butter, and minimal sugar. Avoid products containing hydrogenated oils, artificial flavors, or high-fructose corn syrup, as they diminish nutritional quality.
3. Choose Ethically and Environmentally Certified Products
Opt for chocolates labeled Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or UTZ Certified, ensuring ethical sourcing and reduced exposure to agricultural contaminants. These certifications also support sustainable farming practices for cacao growers.
4. Avoid Heavy Metals
Some dark chocolates contain trace amounts of cadmium and lead, absorbed from the soil during cocoa cultivation. A Consumer Reports (2024) test found most bars had detectable levels of these metals—some exceeding safe daily limits.
To reduce risk, choose brands with third-party testing, avoid ultra-dark (90%+) varieties if eaten often, and limit intake to about 1 oz per day.
Harvard Health Publishing advises selecting reputable, tested products to enjoy dark chocolate safely.
5. Mind the Sugar and Fat Content
Even high-quality dark chocolate can vary in sugar and fat levels. Look for bars with less than 8 grams of sugar per ounce, and prioritize those using natural sweeteners (e.g., coconut sugar, stevia) in small amounts.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions

While dark chocolate can offer heart, brain, and metabolic support, overconsumption or poor-quality products may lead to unwanted effects. Understanding these risks helps you enjoy its benefits safely and responsibly.
Dark chocolate contains caffeine and theobromine, two natural stimulants that may cause restlessness, rapid heartbeat, or sleep disruption in sensitive individuals. The Cleveland Clinic (2025) recommends enjoying it earlier in the day and keeping portions around 1 ounce (28 g) daily to prevent overstimulation.
Some dark chocolates also contain added sugars, which can reduce their nutritional value and negatively affect blood sugar levels. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health advises choosing bars with 70–85% cocoa content and less than 8 g of sugar per serving for optimal health balance.
Although rare, food allergies may occur—especially when dark chocolate is processed with milk, soy, or nuts. The Mayo Clinic recommends checking ingredient labels carefully and avoiding cross-contaminated products if you have known allergies.
Another concern is trace heavy metals, such as cadmium and lead, which cacao plants can absorb from the soil. A Consumer Reports (2023) study found that several dark chocolate brands exceeded safe daily limits when consumed in large amounts. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) notes that heavy metal content varies depending on cocoa origin and processing, so choosing trusted brands that publish third-party safety testing is key.
To minimize risks, select high-cocoa, low-sugar, and verified brands, enjoy 1 oz (28 g) daily, and avoid eating dark chocolate late in the evening. This evidence-based approach lets you experience its benefits safely as part of a balanced, health-conscious diet.
Recommended Daily Intake and Storage Tips
To enjoy dark chocolate responsibly and safely, pay attention to serving size, quality, and proper storage. These steps maintain its flavor and nutritional integrity.
Ideal Daily Portion
- Serving size: About 1 oz (28 g) of 70–85% cocoa dark chocolate per day.
- This portion delivers antioxidants and minerals without excessive sugar or calories.
- Research from the Cleveland Clinic supports small daily servings for balanced heart health benefits.
Storage Guidelines
Follow FDA Food Safety recommendations for best preservation:
- Temperature: Store at 60–70 °F (15–21 °C) in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid refrigeration: Condensation can cause “sugar bloom,” affecting texture.
- Shelf life: Unopened bars last up to 12 months; consume opened bars within 3 months.
Refer to FDA Food Safety and Storage Guidelines for detailed storage advice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How much dark chocolate is safe to eat daily?
About 1 oz (28 g) per day of 70% or higher cocoa dark chocolate is considered a balanced amount.
2. Can dark chocolate support heart health?
Yes, cocoa flavanols may support healthy blood pressure and circulation, as confirmed by the Cleveland Clinic.
3. Is dark chocolate safe for people with diabetes?
When low in sugar and eaten in moderation, dark chocolate may support blood sugar stability, according to the Diabetes Research & Wellness Foundation.
4. What is the healthiest cocoa percentage?
Aim for 70–85% cocoa, which provides the highest flavanol content and lowest added sugar.
5. Does dark chocolate help reduce stress?
Yes. Cocoa flavonoids may promote calmness and stress resilience. Harvard Health Publishing supports moderate consumption for mood balance.
6. Are There Any Risks Related to Heavy Metals in Dark Chocolate?
Some dark chocolates may contain trace levels of cadmium and lead absorbed from soil. A Consumer Reports (2023) test found most brands had detectable amounts—some exceeding safe limits. Choose tested, reputable brands and limit intake to about 1 oz daily for safe enjoyment.
7. Can children eat dark chocolate?
Small amounts are generally safe, but due to caffeine and sugar, it’s best limited for young children. Consult a pediatric dietitian if unsure.
Conclusion
Dark chocolate, when chosen wisely and enjoyed in moderation, can be a nutrient-rich addition to a healthy lifestyle. Its flavanols and antioxidants support cardiovascular, cognitive, and metabolic wellness while offering a satisfying, mindful indulgence.
Always opt for high-cocoa, low-sugar, and ethically sourced varieties to maximize benefits and minimize risks. Combine it with a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for best results.
This content is for informational purposes only and not medical advice.
References:
- Cleveland Clinic – Dark Chocolate Health Benefits
Guidance on portion size, caffeine sensitivity, and timing for safe dark chocolate consumption. - Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – The Nutrition Source: Dark Chocolate
Explains cocoa percentage, sugar content, and how to select healthier varieties of dark chocolate. - Consumer Reports (2023) – Lead and Cadmium in Dark Chocolate
Independent lab testing on heavy metal contamination across major dark chocolate brands. - National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Heavy Metal Analysis of Chocolate Products (2024)
Peer-reviewed analysis of cadmium and lead content variations in global cocoa sources.
