Arugula may support heart, bone, and metabolic health thanks to its rich supply of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds.
This peppery green from the cruciferous family is a powerhouse of nutrition and antioxidants that support overall wellness. Understanding its evidence-backed benefits helps you make smarter dietary choices for long-term health.

What Is Arugula? (Overview and Nutrition Profile)
Arugula (Eruca sativa)—also known as rocket or rucola—is a leafy green vegetable from the Brassicaceae family, the same plant group as kale, broccoli, and mustard greens.
It’s celebrated for its distinct peppery flavor, tender leaves, and high nutrient density, making it a staple in Mediterranean and health-conscious diets.
Arugula grows best in cool climates and is widely cultivated across Europe and North America. It’s commonly used raw in salads, wraps, and smoothies, or lightly wilted in pasta and grain bowls. Beyond flavor, its value lies in its rich concentration of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive plant compounds that support heart, bone, and immune health.
Nutritional Profile (Per 1 cup raw, ~20 g)
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 5 kcal | 0% |
| Carbohydrates | 0.7 g | <1% |
| Protein | 0.5 g | 1% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.3 g | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 21.8 µg | 18% |
| Vitamin A | 475 IU | 10% |
| Vitamin C | 1.5 mg | 2% |
| Folate | 19 µg | 5% |
| Calcium | 32 mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 74 mg | 2% |
*Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
(Source: USDA FoodData Central – Arugula, Raw, 2024)
10 Proven Health Benefits of Arugula (Backed by Science)
Arugula is more than just a flavorful salad green—it’s a nutrient-dense powerhouse that supports cardiovascular, bone, metabolic, and immune health.
Packed with natural nitrates, vitamin K, and plant compounds called glucosinolates, arugula offers broad wellness benefits backed by credible scientific research.
1. Supports Cardiovascular Health

Arugula is rich in dietary nitrates, which the body converts into nitric oxide, a compound that helps relax blood vessels and maintain healthy blood flow.
According to a 2024 study in Frontiers in Nutrition, regular intake of nitrate-rich leafy greens like arugula may help improve endothelial (vessel-lining) function and support normal blood pressure (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024).
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health also emphasizes that diets rich in green leafy vegetables are linked to lower rates of heart disease and stroke (Harvard Nutrition Source).
Tip: Add fresh arugula to salads, pasta, or sandwiches to naturally increase your nitrate and potassium intake—both essential for cardiovascular support.
2. Supports Bone Health via Vitamin K and Calcium

Arugula provides a meaningful amount of vitamin K, essential for activating osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium in bones.
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (2023) notes that adequate vitamin K intake is associated with stronger bone mineral density and lower fracture risk (Harvard Nutrition Source – Vitamin K).
With calcium and magnesium, arugula supports overall skeletal integrity and muscle function—especially important for aging adults and postmenopausal women.
Tip: Combine arugula with olive oil or avocado to improve absorption of its fat-soluble nutrients like vitamin K and carotenoids.
3. May Support Cancer-Protective Pathways
As a cruciferous vegetable, arugula contains glucosinolates, which the body converts into isothiocyanates such as sulforaphane.
These compounds help activate enzymes that support cellular detoxification and oxidative defense systems.
A 2023 review in Molecules found that higher intake of cruciferous vegetables correlates with lower incidence of several cancer types, particularly those of the digestive tract and lungs (National Institutes of Health – PubMed Central).
Including arugula in your weekly diet contributes to a protective plant-based eating pattern recognized by the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) (AICR Recommendations).
4. Rich in Antioxidants That Support Cellular Health

Arugula’s vitamin C, polyphenols, and flavonoids help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and supporting immune balance.
According to Medical News Today (2024), frequent consumption of leafy greens is linked to lower inflammation markers and improved immune regulation (Medical News Today).
Its antioxidant profile also supports collagen production and tissue repair.
Tip: Pair arugula with vitamin C-rich foods like citrus or bell peppers to enhance iron absorption and antioxidant synergy.
5. May Support Healthy Blood Sugar Regulation

Emerging studies suggest that arugula extract may help support glucose regulation by improving insulin sensitivity and slowing carbohydrate digestion.
Animal research published in Frontiers in Pharmacology (2023) observed improvements in blood sugar metabolism among subjects consuming cruciferous vegetable extracts (Frontiers in Pharmacology).
Though human studies are still developing, including arugula in balanced meals with protein and fiber may help stabilize post-meal glucose levels.
Tip: Combine arugula with complex carbohydrates like quinoa or brown rice to promote steady energy and satiety.
6. Supports Eye and Skin Health
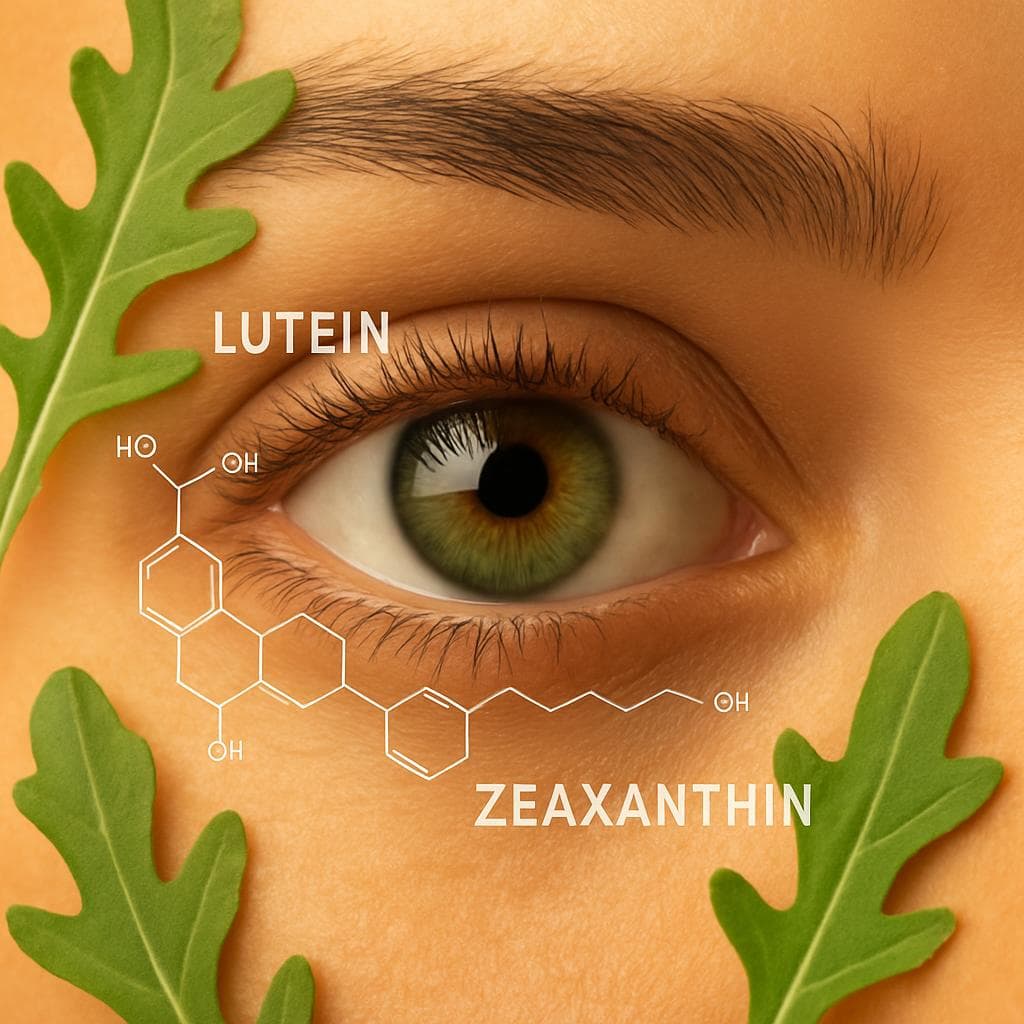

Arugula is naturally rich in beta-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin—powerful antioxidants that may support both eye and skin health. These carotenoids help protect the retina from oxidative stress and filter high-energy blue light, which can contribute to age-related eye damage.
According to the National Eye Institute (NEI), lutein and zeaxanthin are the only dietary carotenoids found in significant quantities in the retina and may help reduce the risk of progression in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) (National Eye Institute – Eye Health and Supplements).
In addition, arugula’s vitamin A content supports normal skin cell renewal, barrier protection, and moisture balance, helping maintain healthy, radiant skin. Vitamin A also plays a role in regulating keratin production—essential for smooth, resilient skin.
7. Supports Immune Function

Arugula provides an immune-boosting blend of vitamin C, folate, and polyphenols.
Vitamin C helps strengthen white blood cell function, while folate aids DNA synthesis in immune cells.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasizes that fruits and vegetables high in vitamins A and C support the body’s natural defense mechanisms (CDC – Nutrition Basics).
Regular inclusion of arugula in meals can thus support immune readiness year-round.
8. May Support Healthy Weight and Digestion

Arugula is low in calories yet naturally high in dietary fiber, making it an excellent choice for supporting healthy digestion and weight management. Fiber adds bulk to meals, helping promote satiety and regular bowel movements, while its prebiotic properties nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
Its natural bitter compounds also stimulate digestive enzyme secretion and bile flow, which may aid fat metabolism and nutrient absorption.
According to Harvard Health Publishing, a diet rich in high-fiber vegetables supports gut microbiome diversity and helps maintain metabolic balance, both of which are key for healthy weight control and reduced inflammation (Harvard Health Publishing – Fiber and Gut Health).
Tip: Enjoy a handful of fresh arugula before your main meal or as a side salad to boost fullness, improve digestion, and support your overall gut health naturally.
9. May Support Liver and Detoxification Processes
Cruciferous vegetables such as arugula contain indole-3-carbinol and sulforaphane, compounds that enhance phase II liver enzymes involved in natural detoxification.
According to Frontiers in Nutrition (2024), these phytonutrients support antioxidant defenses and may protect liver cells from oxidative damage (Frontiers in Nutrition).
Including arugula, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts regularly can help maintain balanced liver metabolism.
10. May Support Cognitive Function and Healthy Aging
Arugula’s nitrates may help increase cerebral blood flow, while its antioxidants combat oxidative stress in brain tissue.
A 2023 review in Nutrients found that diets rich in leafy greens are linked to slower age-related cognitive decline and improved memory performance (Nutrients Journal).
This makes arugula a valuable addition to a brain-healthy eating pattern, alongside omega-3-rich foods and whole grains.
How to Use Arugula in Your Diet

Arugula’s sharp, peppery taste makes it one of the most versatile greens to include in everyday meals. It pairs beautifully with sweet, tangy, or rich ingredients, adding a refreshing contrast while boosting nutrient density.
Practical Ways to Enjoy Arugula
- Salads: Combine arugula with spinach, cherry tomatoes, citrus fruits, nuts, and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Smoothies: Blend a handful with banana, apple, or pineapple for a mild peppery edge and extra vitamins.
- Pesto: Replace basil with arugula for a bolder flavor; mix with olive oil, garlic, nuts, and Parmesan.
- Sandwiches & Wraps: Layer arugula with lean proteins like turkey or tofu for texture and nutrients.
- Soups & Pasta: Stir in at the end of cooking for a burst of freshness and antioxidants.
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health’s Healthy Eating Plate recommends making vegetables—especially dark leafy greens—a major part of your daily meals (Harvard Healthy Eating Plate).
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Arugula is safe for most people when eaten in moderation as part of a balanced diet. However, some of its nutrients and natural compounds may require attention for specific individuals. The following considerations are based on authoritative, up-to-date health sources and presented in a factual, non-medical manner.
Vitamin K and Blood Thinner Interaction
Arugula is naturally high in vitamin K, an essential nutrient for normal blood clotting and bone health. For individuals taking warfarin (Coumadin) or other anticoagulant medications, sudden changes in vitamin K intake may affect medication efficacy.
According to Harvard Health Publishing, people using blood thinners should maintain a consistent intake of vitamin K–rich foods like leafy greens rather than avoid them. Regular monitoring with a healthcare professional ensures balanced clotting control while still benefiting from nutrient-dense vegetables (Harvard Health Publishing – Vitamin K and Warfarin).
High Nitrate Considerations
Arugula, like spinach and lettuce, can naturally accumulate nitrates from soil and fertilizer. In moderate amounts, dietary nitrates from vegetables can help support healthy blood pressure and vascular function by aiding nitric oxide production.
However, excessive nitrate exposure—especially from contaminated sources or improper storage—can pose health risks. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) emphasizes that while arugula (rocket) often contains higher nitrate levels than other vegetables, the overall benefits of vegetable consumption far outweigh potential risks when stored and consumed properly (EFSA – Nitrates in Vegetables).
Tip: Choose fresh, crisp arugula, rinse thoroughly, and refrigerate at 40 °F (4 °C) or below to maintain safety and nutrient quality.
Rare Allergic Reactions
Although uncommon, some people may experience mild allergic reactions to arugula—especially if they are sensitive to other cruciferous vegetables like mustard greens, cabbage, or broccoli. Symptoms can include itching, mild swelling, or digestive discomfort.
The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) advises stopping consumption and consulting a qualified allergist or healthcare provider if allergy symptoms occur (AAAAI – Food Allergy Overview).
Storage and Food Safety Tips
Proper handling keeps arugula fresh, flavorful, and safe to eat. Like all leafy greens, arugula can carry surface bacteria from soil or irrigation water, so following safe washing and refrigeration practices is essential for preventing foodborne illness.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), consumers should always follow the four key steps of safe food handling — Clean, Separate, Cook, and Chill — to reduce contamination risk (FDA – Safe Food Handling).
- Washing: Rinse arugula thoroughly under clean, running water before eating or cooking. Avoid using soap, bleach, or chemical produce washes, as these are not approved for food use.
- Drying: Pat leaves dry with paper towels or use a salad spinner to remove moisture and help prevent spoilage.
- Refrigeration: Store arugula in a breathable container or perforated plastic bag in the refrigerator at 40 °F (4 °C) or below to slow bacterial growth and preserve crispness.
- Shelf Life: Use within 3–5 days of purchase for the best taste and nutrient quality.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Keep arugula separate from raw meat, poultry, and seafood—both in storage and during meal prep—to avoid bacterial transfer.
FAQs About Arugula
1. Can pregnant women eat arugula?
Yes—if it’s washed thoroughly to remove dirt or bacteria. Arugula provides folate, which supports fetal neural development.
2. Is raw or cooked arugula more nutritious?
Raw arugula preserves vitamin C and nitrates, while lightly cooked arugula makes carotenoids more bioavailable. Both are beneficial.
3. How often should I eat arugula?
Including a handful several times per week is a simple way to boost your intake of vitamins A, K, and C.
4. Does arugula help with digestion?
Yes—its fiber supports gut motility and beneficial bacteria, aiding regularity.
5. Can people with thyroid issues eat arugula?
In moderation, yes. Arugula’s goitrogen content is lower than that of broccoli or kale, and cooking reduces it further.
6. Is arugula good for detox diets?
It may support natural detoxification enzymes in the liver, but no food alone “detoxifies” the body; focus on a balanced diet and hydration.
7. Can children eat arugula?
Yes, but its peppery flavor may be strong for some—mix with milder greens like spinach or romaine.
Conclusion
Arugula is a flavorful, nutrient-dense leafy green that supports multiple aspects of wellness—from heart and bone health to digestion and skin vitality.
Its blend of vitamin K, calcium, nitrates, and antioxidants makes it one of the most valuable greens to include in a balanced, plant-forward diet.
Whether tossed in salads, blended into smoothies, or added to warm dishes, arugula offers a simple way to elevate both the flavor and nutrition of your meals.
This content is for informational purposes only and not medical advice.
References:
- EFSA Scientific Opinion – Nitrate in Vegetables (EFSA Journal, 2017)
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) – Food Allergy Overview
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – Safe Food Handling
