The best dumbbell workouts for men build strength, muscle, and athletic power — no gym required.
Whether you train at home or in the gym, dumbbells offer the versatility to target every muscle group through a full range of motion.

Understanding how to structure your dumbbell workouts helps you train efficiently, boost testosterone naturally, and improve overall body composition. This guide covers 15 of the most effective dumbbell exercises — backed by recent strength-training research and expert programming principles.
Dumbbell training enhances balance, coordination, and stability while promoting symmetrical strength development. You’ll find workouts suitable for all levels, focusing on compound and isolation moves to build a complete physique.
Why Dumbbell Workouts Work for Men
Research consistently shows that dumbbell training provides equal or greater muscle activation compared to barbell or machine training.
A 2020 Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research study found no difference in hypertrophy outcomes between free weights and machines when training volume and intensity were matched.
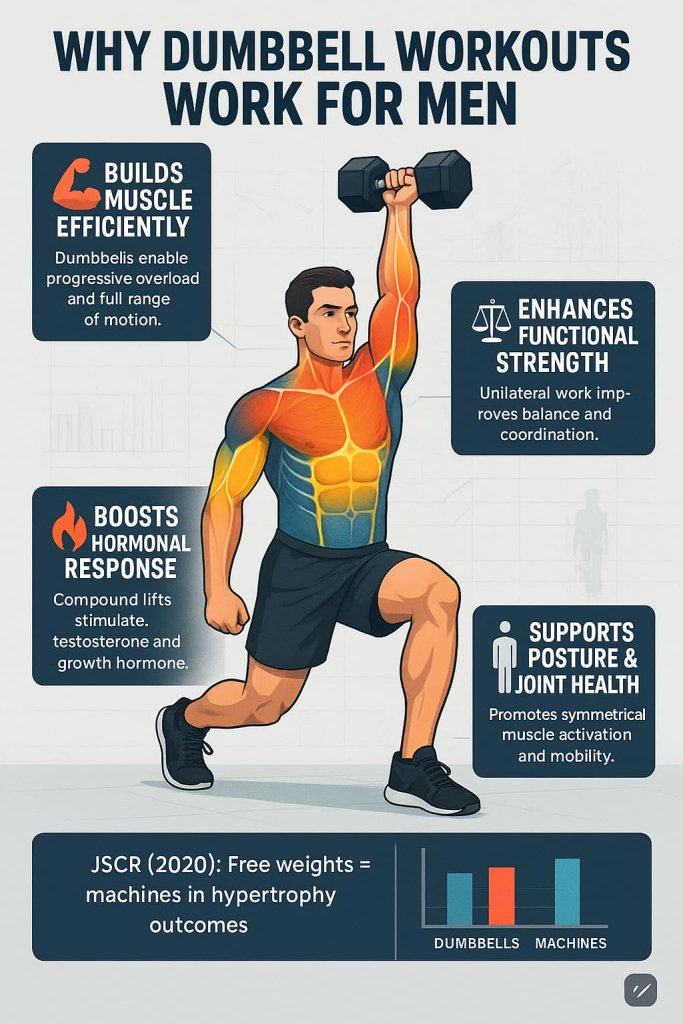
Key Benefits:
- Builds muscle mass efficiently: Ideal for progressive overload and hypertrophy.
- Enhances functional strength: Improves balance and joint stability through unilateral (one-sided) work.
- Increases hormonal response: Compound dumbbell lifts naturally raise testosterone and growth hormone levels.
- Supports posture and joint health: Encourages controlled motion and muscle symmetry.
How to Structure Dumbbell Workouts
| Training Variable | Recommended Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 3–4 sessions/week | Optimal recovery and growth |
| Reps | 8–12 (hypertrophy), 12–15 (endurance) | Muscle size and conditioning |
| Sets | 3–4 per exercise | Effective volume for results |
| Rest | 45–90 seconds | Balanced recovery and intensity |
| Progression | Gradually increase load or reps | Continuous adaptation |
Pro Tip: Track your lifts weekly. Even a 2-5% increase in dumbbell weight signals strength progression.
15 Best Dumbbell Workouts for Men
Each exercise below includes purpose, primary muscles worked, and step-by-step guidance.
1. Dumbbell Bench Press
Why it works:
The dumbbell bench press is one of the most effective upper-body builders for men. Unlike the barbell version, it allows each arm to move independently, reducing muscular imbalances and improving shoulder joint stability. The greater range of motion also activates more chest fibers, leading to enhanced muscle growth and definition.
Muscles worked:
Pectoralis major, anterior deltoids, triceps brachii, and core stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Lie flat on a bench with feet planted firmly on the ground.
- Hold dumbbells directly above your chest with palms facing forward.
- Slowly lower the weights until your elbows reach a 90° angle or slightly below chest level.
- Press the dumbbells upward in a controlled motion, exhaling as you push.
- Avoid locking out elbows at the top to maintain tension on the chest.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your shoulder blades retracted (pulled back) throughout the movement to protect your rotator cuff and increase pec engagement. Focus on squeezing your chest at the top of each rep.
2. Dumbbell Goblet Squat
Why it works:
The goblet squat teaches proper squatting mechanics and strengthens your legs, glutes, and core simultaneously. It’s ideal for beginners learning hip mobility and posture control while also providing a deep leg stimulus for advanced lifters.
Muscles worked:
Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, core, and erector spinae.
How to do it:
- Hold one dumbbell vertically against your chest with both hands under the top plate.
- Keep your chest up and back straight.
- Lower your hips until your thighs are parallel (or slightly below parallel) to the floor.
- Drive through your heels to return to standing.
- Keep knees aligned with toes throughout.
Trainer Tip:
Push your knees outward slightly on the way down to engage glutes and prevent knee cave-in. If flexibility is limited, elevate your heels slightly on plates.
3. Dumbbell Shoulder Press
Why it works:
This classic pressing movement develops shoulder mass, power, and functional mobility. Dumbbells allow a natural pressing arc that reduces shoulder impingement risk compared to a straight barbell press.
Muscles worked:
Anterior and lateral deltoids, triceps, and upper trapezius.
How to do it:
- Sit on a bench with back support (or stand for added core activation).
- Hold dumbbells at shoulder height, palms facing forward.
- Press the weights overhead until your arms are nearly straight.
- Slowly lower back to the starting position under control.
Trainer Tip:
Avoid arching your lower back — squeeze your glutes and brace your core for stability. Think of pressing “up and slightly in” rather than straight up to follow your shoulder’s natural motion path.
4. Dumbbell Bent-Over Row
Why it works:
An essential compound lift for developing a strong, muscular back. It trains both the lats and upper back, improving posture, shoulder health, and pulling strength.
Muscles worked:
Latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, posterior deltoids, biceps, and erector spinae.
How to do it:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding dumbbells with palms facing in.
- Hinge at your hips until your torso is nearly parallel to the floor.
- Keep your back flat and chest lifted.
- Pull the dumbbells toward your waist, squeezing shoulder blades together.
- Lower slowly until arms are fully extended.
Trainer Tip:
Don’t round your back — think of pulling with your elbows, not your hands. This helps isolate the back muscles and reduces arm dominance.
5. Dumbbell Romanian Deadlift
Why it works:
Targets the posterior chain — the foundation of power and athletic performance. This move enhances hamstring flexibility and glute strength, improving posture and reducing lower-back pain risk.
Muscles worked:
Hamstrings, glutes, erector spinae, and core stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells in front of your thighs with palms facing your body.
- Hinge at your hips, keeping a slight bend in your knees.
- Lower dumbbells down the front of your legs until you feel a hamstring stretch.
- Push hips forward to return to standing, squeezing glutes at the top.
Trainer Tip:
Keep dumbbells close to your legs throughout the movement — imagine “dragging” them along your thighs. Move slowly; this exercise is about tension, not speed.
6. Dumbbell Lunge
Why it works:
Lunges train balance, coordination, and unilateral strength. They’re excellent for fixing leg imbalances while also activating stabilizing muscles in your hips and core.
Muscles worked:
Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and calves.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells at your sides.
- Step forward and lower your body until both knees form 90° angles.
- Push through your front heel to return to standing.
- Alternate legs each rep.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your front knee directly above your ankle. Avoid pushing off with your back leg — your front leg should do most of the work.
7. Dumbbell Bicep Curl
Why it works:
A staple for arm development, curls isolate the biceps while engaging stabilizers in the shoulders and forearms. Excellent for both strength and aesthetics.
Muscles worked:
Biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis.
How to do it:
- Stand tall with arms at sides and palms facing forward.
- Keep elbows pinned close to your torso.
- Curl the dumbbells up toward your shoulders.
- Lower slowly to maximize muscle engagement.
Trainer Tip:
Don’t swing the weights — focus on a 2-second upward movement and a 3-second controlled lowering phase for best hypertrophy results.
8. Dumbbell Triceps Kickback
Why it works:
A precision isolation move that tones and strengthens the back of the arm. It’s particularly effective when done with strict form.
Muscles worked:
Triceps brachii.
How to do it:
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand and hinge at your hips until torso is parallel to the floor.
- Keep elbows tight to your body.
- Extend arms backward until fully straight.
- Pause briefly, then return slowly to start.
Trainer Tip:
Don’t let your upper arms move — lock them in place. The only motion should come from the elbow joint.
9. Dumbbell Fly
Why it works:
This move isolates the chest and emphasizes the stretch at the bottom of the motion — critical for shaping the pectorals and increasing muscle definition.
Muscles worked:
Pectoralis major, anterior deltoids.
How to do it:
- Lie flat on a bench, arms extended above chest with slight bend in elbows.
- Open arms wide in a controlled arc until you feel a deep stretch.
- Bring dumbbells back over chest by squeezing pecs.
Trainer Tip:
Use moderate weights to protect your shoulder joints. Focus on the stretch and contraction — not the load.
10. Dumbbell Step-Up
Why it works:
A powerful lower-body movement that mimics real-life athletic motion. It develops strength, balance, and functional mobility.
Muscles worked:
Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, calves, and core.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells at your sides.
- Step onto a bench or box with one leg.
- Push through your heel to stand tall.
- Slowly lower back down and switch sides.
Trainer Tip:
Choose a step height where your knee reaches roughly 90°. Keep the torso upright and avoid using momentum.
11. Dumbbell Shrug
Why it works:
Targets the trapezius muscles responsible for neck and upper back strength. Ideal for improving posture and shoulder health.
Muscles worked:
Trapezius, levator scapulae.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells at your sides with straight arms.
- Shrug shoulders upward as high as possible.
- Hold for 1–2 seconds before lowering slowly.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your arms straight and move vertically — avoid shoulder rolls, which can cause joint irritation.
12. Dumbbell Farmer’s Carry
Why it works:
This full-body functional exercise enhances grip endurance, posture, and overall core stability. It’s also an underrated fat-burning finisher.
Muscles worked:
Forearms, traps, shoulders, core, and glutes.
How to do it:
- Pick up two heavy dumbbells and hold them at your sides.
- Walk forward 20–40 meters with your core tight and shoulders pulled back.
- Maintain upright posture throughout.
Trainer Tip:
Think “tall and tight.” Engage your core and keep your ribs down to avoid lower-back strain.
13. Dumbbell Lateral Raise
Why it works:
Sculpts broader shoulders and enhances the visual width of the upper body. Perfect for creating a balanced, V-shaped look.
Muscles worked:
Lateral deltoids, supraspinatus.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells at sides, palms facing inward.
- Raise arms out to sides until they reach shoulder height.
- Pause briefly and lower slowly under control.
Trainer Tip:
Slightly bend your elbows and lead with them, not your hands. Perform slow, controlled reps — quality over quantity.
14. Dumbbell Hammer Curl
Why it works:
This biceps variation increases overall arm thickness while strengthening the forearms and grip. The neutral wrist position reduces stress on the elbows.
Muscles worked:
Brachialis, brachioradialis, biceps brachii.
How to do it:
- Hold dumbbells with palms facing each other.
- Curl both weights up simultaneously or alternately.
- Lower slowly while maintaining control.
Trainer Tip:
Keep wrists neutral and avoid elbow flare. For advanced progression, use a slow eccentric phase to enhance time under tension.
15. Dumbbell Bulgarian Split Squat
Why it works:
A superior single-leg exercise that builds strength, balance, and coordination. It deeply targets the quads and glutes for athletic lower-body development.
Muscles worked:
Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, core stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Stand about two feet in front of a bench.
- Rest your back foot on the bench behind you.
- Lower your hips until your front thigh is parallel to the floor.
- Push through your front heel to rise back up.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your torso upright and core engaged. Drive evenly through your front heel to avoid knee strain and maximize glute activation.
Safety and Precautions
- Always warm up with light cardio and dynamic stretches.
- Maintain proper posture—avoid arching or twisting during lifts.
- Use controlled movements; avoid swinging the weights.
- Stop immediately if you feel sharp pain or joint discomfort.
- Start light and gradually increase resistance.
FAQ
1. Can I build muscle with only dumbbells?
Yes. Progressive overload and proper nutrition make dumbbell training sufficient for muscle growth.
2. How often should I do dumbbell workouts?
3–4 sessions per week with at least 48 hours between same-muscle training.
3. What’s the best dumbbell weight for beginners?
Start with weights you can lift for 10–12 reps while maintaining perfect form.
4. Are dumbbells better than barbells?
Both are effective; dumbbells improve stability and correct imbalances.
5. Should I train full body or split routines?
Beginners benefit from full-body workouts, while advanced lifters can split by muscle group.
6. How long before I see results?
Consistent training and balanced nutrition typically show visible changes within 6–8 weeks.
7. Do dumbbell workouts burn fat too?
Yes — resistance training raises metabolism and promotes fat oxidation for hours post-workout.
Conclusion
Dumbbell workouts for men deliver one of the most efficient, versatile ways to gain size, power, and confidence. With the 15 proven exercises above, you can train every muscle effectively — anywhere, anytime.
Start light, master your form, and progress gradually for long-term strength and physique results.
Ready to begin? Grab your dumbbells and build your strongest self today.
References
- Free Weights vs. Machines (RCT, 2020) — Shows hypertrophy/strength can be comparable when volume/intensity are matched → supports dumbbells for size & strength.
Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research (PubMed) - Training Frequency & Hypertrophy (Meta-analysis, 2016) — Guides weekly frequency (e.g., 2–3+ hits per muscle) for growth.
Sports Medicine (PubMed) - Deadlift Variants & EMG (2020) — Confirms strong hamstring/posterior-chain activation; useful for your Dumbbell RDL cues.
Open-access full text (PMC) - Unilateral vs. Bilateral Training (Meta-analysis, 2023) — Supports lunges, split squats, step-ups for asymmetry & performance.
Frontiers in Physiology - Loaded Carries Muscle Activation (2024) — Quantifies core/trap activation during carries; backs Farmer’s Carry section.
Open-access full text (PMC) - ACSM Position Stand: Progression Models (Foundational) — Gold-standard guidance for sets, reps, rest, progression (safety/YMYL).
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise (PubMed) - Warm-Up: Mechanisms & Applications (Review) — Rationale for dynamic warm-ups before lifting; supports your Warm-Up H2.
Sports Medicine (open summary via PMC-linked review) - Consumer Safety & Getting Started (2023) — Clear, accessible YMYL guidance on reps/sets and safe progression for readers.
Harvard Health Publishing
