Kettlebell workouts for men build strength, power, and muscle faster than traditional training by combining resistance and dynamic movement.
This hybrid style activates multiple muscle groups, enhances cardiovascular fitness, and promotes functional strength that translates to real-world performance.
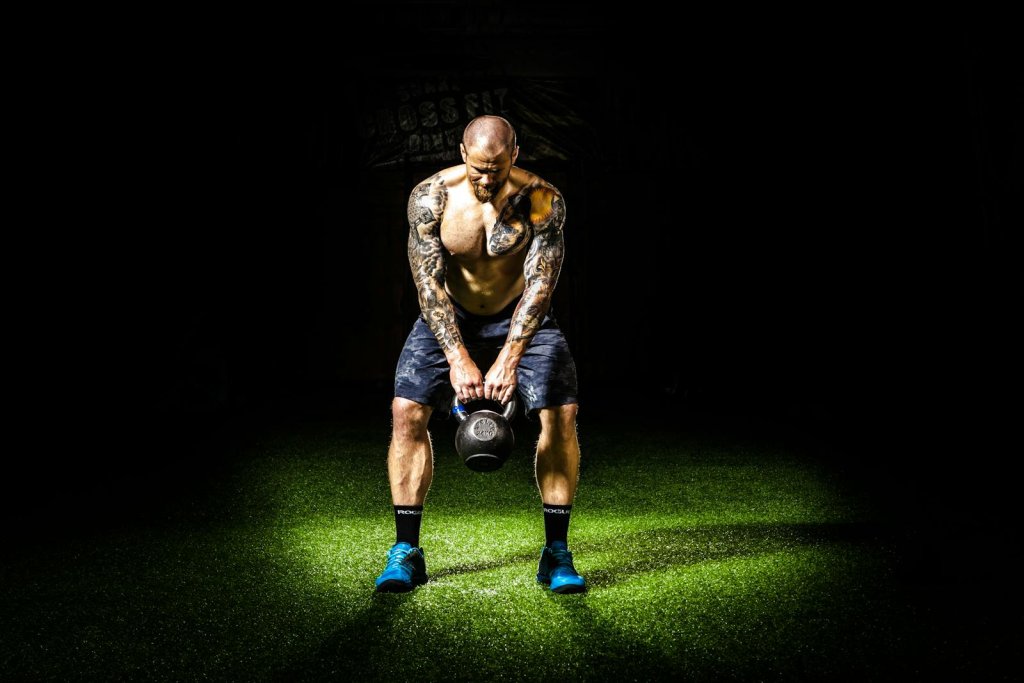

Kettlebells challenge your balance, grip, and core stability — making them ideal for men who want to build muscle, burn fat, and move athletically without spending hours in the gym. According to Experts, kettlebell training improves both muscular endurance and explosive power when programmed strategically.
Let’s break down the best 16 kettlebell workouts to help you build lean muscle, strength, and agility — safely and efficiently.
Benefits of Kettlebell Workouts for Men
- Full-Body Engagement: Activates major muscle groups simultaneously for more efficient training.
- Functional Strength: Builds coordination, mobility, and joint stability.

- Power and Conditioning: Ballistic moves like swings and snatches develop explosive power.
- Time-Efficient: Combines cardio and strength training in a single session.
- Core Stability: Every movement engages your abs and back for a stronger, more stable core.
Research from NIH shows that kettlebell complexes can boost testosterone and growth hormone naturally through high-intensity resistance output.
How to Warm Up Before Kettlebell Workouts
A good warm-up improves circulation, joint mobility, and safety.
Try this 5-minute sequence:
- Arm circles (30 sec)
- Hip hinges (30 sec)
- Bodyweight squats (1 min)
- Light kettlebell deadlifts (10 reps)
- Kettlebell halos (5 reps each direction)
Trainer Tip: Keep movements dynamic — not static stretching. Focus on engaging your core and glutes before lifting.
16 Best Kettlebell Workouts for Men
Each movement below lists: Why it works, Muscles worked, How to do it, and a Trainer Tip for safe and effective execution.
1. Kettlebell Swing
Why it works:
The kettlebell swing is a cornerstone of power training. It builds explosive hip drive and strengthens the posterior chain — glutes, hamstrings, and lower back — while improving cardiovascular endurance.
Muscles worked: Glutes, hamstrings, lower back, core, forearms.
How to do it:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, bell about a foot in front of you.
- Hinge at the hips, grab the handle, and swing it between your legs.
- Explosively extend your hips to propel the bell to chest height.
- Let gravity bring it down and repeat with rhythm and control.
Trainer Tip: Keep your arms relaxed and power the movement from your hips, not your shoulders. Maintain a flat back throughout.
2. Goblet Squat
Why it works:
This move strengthens your legs and core while promoting perfect squat form. Holding the kettlebell at your chest helps engage your upper body for balance and posture correction.
Muscles worked: Quads, glutes, hamstrings, core.
How to do it:
- Hold the kettlebell by the horns close to your chest.
- Keep your chest tall and elbows pointed down.
- Lower until your thighs are parallel (or slightly below).
- Drive through your heels to return to standing.
Trainer Tip: Push your knees out and avoid letting your heels lift off the floor.
3. Kettlebell Deadlift
Why it works:
A fundamental strength builder that targets the glutes and hamstrings while teaching proper hip-hinge mechanics. Ideal for both beginners and advanced lifters.
Muscles worked: Glutes, hamstrings, traps, lower back.
How to do it:
- Stand over the kettlebell with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hinge your hips back and bend knees slightly.
- Grab the handle and lift by extending hips and knees.
- Lower slowly under control.
Trainer Tip: Keep your chest up and core braced to avoid rounding your back.
4. Kettlebell Clean
Why it works:
Improves coordination, grip, and transition power — setting up for presses or squats. It also trains explosive hip extension and shoulder stability.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, traps, glutes, biceps, forearms.
How to do it:
- Swing the kettlebell from between your legs up to your shoulder in one motion.
- Rotate your wrist so the bell rests softly on your forearm (rack position).
- Return smoothly to the swing position.
Trainer Tip: Keep the bell close to your body and move fluidly to prevent wrist bruising.
5. Kettlebell Press
Why it works:
Enhances upper-body pressing strength while demanding core and glute stabilization.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, triceps, upper chest, core.
How to do it:
- From rack position, brace your core and press the bell overhead.
- Fully extend your arm with palm forward.
- Lower under control back to rack position.
Trainer Tip: Avoid leaning back. Tighten your core and squeeze glutes before pressing.
6. Kettlebell Snatch
Why it works:
A powerful full-body exercise that combines strength, endurance, and coordination. It improves grip and explosiveness similar to Olympic lifts.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, traps, glutes, hamstrings, core.
How to do it:
- Start with a swing and pull the bell upward in one motion.
- As it rises, rotate your wrist and punch overhead.
- Lock out your arm with the bell above your head, then lower safely.
Trainer Tip: Focus on smooth motion and proper timing — avoid slamming the bell onto your wrist.
7. Kettlebell Lunge Press
Why it works:
Develops single-leg strength, balance, and coordination while integrating an overhead press for total-body engagement.
Muscles worked: Glutes, quads, hamstrings, shoulders, core.
How to do it:
- Hold the kettlebell in rack position.
- Step forward into a lunge and press the bell overhead simultaneously.
- Return to standing and switch legs.
Trainer Tip: Keep your front knee over the ankle and avoid leaning forward.
8. Kettlebell Row
Why it works:
Strengthens your back muscles and improves posture — a must for balancing push-dominant training.
Muscles worked: Lats, rhomboids, traps, biceps.
How to do it:
- Place one hand and knee on a bench (or stay in staggered stance).
- Hold the bell in the other hand and pull toward your waist.
- Lower slowly and repeat.
Trainer Tip: Keep your torso steady — avoid twisting or jerking the bell.
9. Kettlebell High Pull
Why it works:
Enhances shoulder and trap power while training upper-body speed. A great transitional move toward snatches and cleans.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, traps, biceps, core.
How to do it:
- Begin with a two-hand swing.
- As the bell rises, pull elbows high and wide.
- Let the bell drop naturally and repeat.
Trainer Tip: Keep elbows above wrists and maintain a fluid rhythm.
10. Turkish Get-Up
Why it works:
Improves balance, mobility, and total-body stability. It’s one of the most functional exercises for coordination and joint strength.
Muscles worked: Core, shoulders, hips, legs.
How to do it:
- Lie on your back holding the kettlebell overhead.
- Use your free hand to push up, then rise to a standing position step-by-step.
- Reverse the motion to return to lying down.
Trainer Tip: Perform slowly; control each segment to reinforce stability and shoulder safety.
11. Kettlebell Front Rack Squat
Why it works:
Challenges both lower-body strength and core stability, forcing your abs to resist forward collapse.
Muscles worked: Quads, glutes, abs, upper back.
How to do it:
- Hold one or two kettlebells at shoulder height (rack position).
- Keep your chest tall and elbows high.
- Lower into a deep squat, then drive back up.
Trainer Tip: Keep the weight close to your body and breathe out as you stand.
12. Kettlebell Farmer’s Carry
Why it works:
An underrated core and grip strength builder that also enhances posture and shoulder stability.
Muscles worked: Forearms, traps, abs, glutes.
How to do it:
- Hold heavy kettlebells at your sides.
- Walk 20–30 meters with controlled steps and upright posture.
- Keep shoulders pulled back throughout.
Trainer Tip: Tighten your core and avoid leaning to one side.
13. Kettlebell Clean and Press
Why it works:
Combines strength, endurance, and coordination. Excellent for developing full-body conditioning and shoulder stability.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, traps, glutes, triceps, core.
How to do it:
- Clean the kettlebell to rack position.
- Press overhead, then lower with control.
- Return to the swing position and repeat.
Trainer Tip: Use leg drive to assist the press, keeping the core engaged.
14. Kettlebell Russian Twist
Why it works:
Improves rotational strength and core definition while engaging stabilizing muscles in the lower back.
Muscles worked: Obliques, rectus abdominis, lower back.
How to do it:
- Sit with knees bent and lean back slightly.
- Hold the kettlebell close to your chest.
- Rotate your torso side to side, touching the bell near each hip.
Trainer Tip: Move with control — don’t swing your arms; rotate through your core.
15. Kettlebell Windmill
Why it works:
Increases shoulder stability, flexibility, and core strength through controlled rotation and hinge movement.
Muscles worked: Shoulders, obliques, glutes, hamstrings.
How to do it:
- Hold a kettlebell overhead with one arm.
- Turn your feet slightly outward.
- Hinge at the hips and lower your free hand toward the floor.
- Return to standing while keeping the bell locked overhead.
Trainer Tip: Keep eyes on the bell and move slowly for perfect control.
16. Kettlebell Complex (Finisher)
Why it works:
A full-body sequence that builds endurance, coordination, and fat-burning capacity. Excellent for conditioning after strength work.
Muscles worked: Full-body — shoulders, legs, core, back.
How to do it:
- Perform one rep each: swing, clean, press, squat, and snatch.
- Repeat the flow for 3–5 rounds without rest.
Trainer Tip: Choose a moderate weight; focus on smooth transitions and steady breathing.
How Often Should You Train
- Beginners: 2–3 sessions per week (full-body)
- Intermediate/Advanced: 3–5 sessions per week alternating intensity
- Rest Days: 48 hours between heavy sessions for muscle recovery
Experts recommends starting with 16 kg (35 lb) for most men, adjusting based on experience and strength.
Pro Tips for Maximum Results
- Focus on form first, then intensity.
- Don’t rush transitions — control the bell at all times.
- Track reps and gradually increase volume weekly.
- Mix strength-based and ballistic days for balanced development.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using arms instead of hips for swings.
- Overarching the back during presses.
- Neglecting warm-ups or cooldowns.
- Progressing to heavy weights too quickly.
FAQ
1. Are kettlebell workouts enough for total fitness?
Yes. They build strength, power, endurance, and mobility — all in one workout.
2. What size kettlebell should men start with?
Most men start with 12–16 kg (26–35 lb) for beginners and progress to 20–24 kg.
3. Can kettlebells replace dumbbells?
They complement each other — kettlebells offer dynamic, functional strength that dumbbells often miss.
4. How long should a kettlebell workout last?
20–40 minutes is ideal for full-body results.
5. Are kettlebell workouts safe for beginners?
Yes — with proper form and gradual load increases. Always warm up first.
6. Can I build muscle with just kettlebells?
Absolutely. Progressive overload and compound movements stimulate hypertrophy effectively.
7. Do kettlebell workouts burn belly fat?
They increase calorie burn and metabolic rate, aiding fat loss when combined with proper diet.
Conclusion
Kettlebell training gives men a powerful, efficient way to build muscle, strength, and endurance without complicated machines.
Start light, focus on perfect form, and progress consistently — you’ll gain explosive power, athletic conditioning, and functional strength that lasts.
Ready to start? Add 3 of these kettlebell workouts to your weekly routine and feel the difference within weeks.
References
- Enhancing Athletic Performance: A Comprehensive Review on Kettlebell Training (2024) — Evidence that kettlebell training improves strength, power, and conditioning.
Read on PubMed Central - Spine Loads in the Kettlebell Swing, Snatch, and Bottoms-Up Carry (McGill et al., 2012) — Quantifies spinal loading and supports proper hinge/bracing cues.
Read on PubMed - Effects of Kettlebell Training on Aerobic Capacity (2015) — 4-week snatch protocol improved V̇O₂max; supports conditioning claims.
Read on PubMed - ACE-Sponsored Study: Energy Cost & Intensity of Kettlebell Workouts (2010) — Shows high caloric expenditure and vigorous intensity during kettlebell sessions.
Read the ACE Summary - ACE “Do It Better” — Two-Handed Kettlebell Swing (2025) — Technique cues and updated context; notes high kcal/min potential.
Read on ACE - Kettlebell vs. Traditional Resistance Training in Obese Men (BMC Sports Sci, Med & Rehab, 2024) — RCT showing body-composition and fitness improvements.
Read the Open-Access Paper - ACSM Guidance on Session Structure (2025) — Supports warm-up, conditioning, cool-down sequencing for safe programming.
Read the ACSM PDF
