Push-up variations help you build total-body strength, sculpt lean muscle, and progress beyond the basic push-up.
They target the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core — all while improving stability and endurance.
Understanding and practicing different push-up types is key to avoiding plateaus and ensuring balanced development. Whether you’re a beginner or advanced athlete, the right variations can challenge every muscle group and keep your workouts fresh.

Let’s break down 25 of the best push-up variations, from easiest to hardest, with clear instructions and form tips for maximum results.
Why Push-Up Variations Matter
Push-ups are a cornerstone of bodyweight training — they build functional strength and core stability without any equipment.

Research shows that push-up variations (e.g., narrower hand positions, instability, or added resistance) can significantly increase EMG activation of the chest, triceps, and shoulder stabilizers compared with a standard push-up, especially when instability or narrower grips are used.
Sources: Marcolin 2015; Calatayud 2014; Kowalski 2021.
They also improve:
- Muscular balance between upper and lower body
- Joint stability through controlled motion
- Core strength and endurance
- Posture and shoulder health
How to Perform Push-Ups Safely
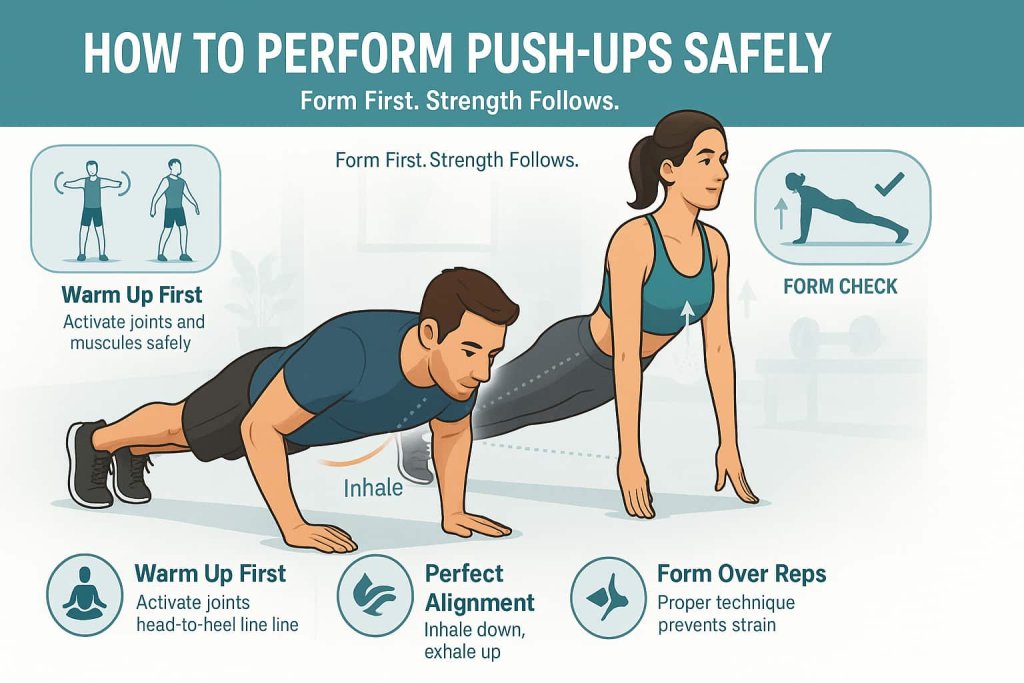
Before exploring variations:
- Warm up with arm circles, planks, and light stretches.
- Maintain a straight line from head to heels.
- Keep your core tight and elbows at a 45-degree angle to your torso.
- Inhale as you lower down, exhale as you push up.
Trainer Tip: Quality over quantity — proper form prevents strain and maximizes strength gains.
25 Best Push-Up Variations (From Beginner to Advanced)
Explore 25 push-up variations that build strength, power, and muscle from the ground up.
Whether you’re a beginner or advanced athlete, these moves challenge every level safely and effectively.
1. Wall Push-Up
Why it works:
This is the most beginner-friendly push-up variation. It reduces bodyweight load to around 15–20% of your weight, helping you learn proper alignment and shoulder mechanics without strain. It’s ideal for older adults, beginners, or those recovering from injury.
Muscles worked:
Chest (pectoralis major), shoulders (anterior deltoids), triceps, and core stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Stand facing a wall about 2 feet away.
- Place your hands flat at shoulder height and shoulder-width apart.
- Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels.
- Bend your elbows and lean your chest toward the wall.
- Pause slightly, then push through your palms to return to the start.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your abs tight and don’t let your lower back sag. As you improve, step further from the wall to increase intensity.
2. Incline Push-Up
Why it works:
By elevating your hands on a bench or sturdy platform, you decrease resistance, making it easier to maintain good form. Perfect for transitioning from wall to floor push-ups.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and core.
How to do it:
- Place your hands on a bench or step, slightly wider than shoulder-width.
- Walk your feet back so your body forms a straight line.
- Lower your chest toward the edge of the bench, then press back up.
Trainer Tip:
Focus on keeping your neck neutral — don’t look down or up. Lower the incline gradually as you get stronger.
3. Knee Push-Up
Why it works:
Reduces the total load by roughly 40%, helping you build strength safely. It’s excellent for beginners or for endurance training.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and abs.
How to do it:
- Start in a plank with knees on the floor.
- Keep your body straight from head to knees.
- Lower your chest toward the floor, then push back up.
Trainer Tip:
Engage your abs and glutes — this prevents arching your back and strengthens your core even in a modified stance.
4. Standard Push-Up
Why it works:
A foundational strength builder that works multiple upper-body muscles and core simultaneously. It also enhances joint stability and coordination.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, abs, and spinal stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Place hands shoulder-width apart, feet hip-width.
- Engage your core and lower your chest until it nearly touches the floor.
- Push back up while maintaining a straight line.
Trainer Tip:
Avoid flaring your elbows too far out; a 45° angle protects your shoulders.
5. Wide-Grip Push-Up
Why it works:
By spreading your hands wider, you increase the stretch and activation of the chest while minimizing triceps involvement.
Muscles worked:
Chest (especially outer fibers), shoulders, and core.
How to do it:
- Assume a push-up position with hands 1.5× shoulder-width apart.
- Lower your chest until it nearly touches the ground.
- Press back up with control.
Trainer Tip:
Move slower and focus on the chest contraction. Don’t drop your hips — maintain tension throughout.
6. Close-Grip Push-Up
Why it works:
A triceps-dominant push-up that also strengthens your inner chest and front shoulders.
Muscles worked:
Triceps, inner chest, and anterior deltoids.
How to do it:
- Set your hands directly under your shoulders.
- Keep elbows tight to your ribs.
- Lower your chest down, then press back up powerfully.
Trainer Tip:
Squeeze your triceps at the top for maximum activation. Keep your elbows from flaring out.
7. Diamond Push-Up
Why it works:
This narrow-hand variation targets triceps more intensely than any other push-up type, making it ideal for arm definition and strength.
Muscles worked:
Triceps, inner chest, shoulders, and core.
How to do it:
- Form a diamond shape with your thumbs and index fingers beneath your chest.
- Lower your torso slowly until your chest nearly touches your hands.
- Push back up.
Trainer Tip:
Go slow — this move is demanding. If too difficult, start on your knees.
8. Staggered Push-Up
Why it works:
Asymmetrical positioning forces each arm to stabilize differently, enhancing coordination and correcting imbalances.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and core stabilizers.
How to do it:
- Place one hand slightly forward, the other slightly back.
- Perform a push-up, keeping hips square.
- Switch hand positions every few reps.
Trainer Tip:
Move your hands just 4–6 inches apart — too wide a stagger can strain your shoulders.
9. Decline Push-Up
Why it works:
Increases resistance and shifts emphasis to the upper chest and shoulders, mimicking an incline bench press.
Muscles worked:
Upper chest, front shoulders, triceps, and abs.
How to do it:
- Place feet on a step or bench, hands on the ground shoulder-width apart.
- Lower your chest to the floor, then push up.
- Maintain a straight line throughout.
Trainer Tip:
Don’t arch your back — engage your core and glutes to stay aligned.
10. Shoulder Tap Push-Up
Why it works:
Combines push-up strength with balance and anti-rotation core control.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, abs, and obliques.
How to do it:
- Perform a push-up.
- At the top, tap your right shoulder with your left hand.
- Alternate sides each rep.
Trainer Tip:
Widen your stance slightly to increase stability and reduce hip sway.
11. Tempo Push-Up
Why it works:
Slow eccentric lowering increases time under tension, boosting muscle growth and control.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, abs.
How to do it:
- Lower your body for 3–4 seconds, pause briefly, then push up explosively.
- Maintain full control of your core.
Trainer Tip:
Use a 3:1 tempo rhythm — three seconds down, one up — to maximize gains.
12. Spiderman Push-Up
Why it works:
Adds a dynamic twist by engaging hip flexors and obliques, building full-body coordination.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, obliques, abs, and hip flexors.
How to do it:
- As you lower, bring your right knee toward your right elbow.
- Return to start and switch sides each rep.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your torso level — avoid twisting your hips outward.
13. T Push-Up
Why it works:
Improves core rotation, shoulder mobility, and balance.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and obliques.
How to do it:
- Perform a push-up.
- At the top, rotate your torso, raising one arm straight up to form a “T.”
- Return and repeat on the other side.
Trainer Tip:
Move slowly and control your rotation to protect your lower back.
14. Archer Push-Up
Why it works:
Simulates a single-arm push-up by loading one side more heavily, improving unilateral strength and control.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and core.
How to do it:
- Start in a wide push-up stance.
- Lower your chest toward one hand while keeping the other arm straight.
- Push back to the starting position and alternate sides.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your hips and shoulders square — avoid rotating.
15. One-Leg Push-Up
Why it works:
Removes one point of contact, increasing core engagement and balance demand.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, glutes, and abs.
How to do it:
- From a standard push-up, lift one leg off the floor.
- Perform a push-up without letting your hips drop.
- Switch legs every few reps.
Trainer Tip:
Engage your glutes and squeeze your abs to stabilize your pelvis.
16. Sphinx Push-Up
Why it works:
A triceps-focused variation that strengthens arms and shoulders without shoulder strain.
Muscles worked:
Triceps, chest, shoulders, abs.
How to do it:
- Begin in a forearm plank.
- Press through your palms to lift into full plank.
- Lower slowly back down.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your elbows tucked close and engage your abs — no sagging hips.
17. Plyometric (Clap) Push-Up
Why it works:
Boosts explosive upper-body power and speed. Great for athletes and fat-burning HIIT routines.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, and abs.
How to do it:
- Lower into a push-up and explode off the floor.
- Clap your hands before landing softly with bent elbows.
Trainer Tip:
Land gently to avoid wrist strain. Master standard push-ups first.
18. Hindu Push-Up
Why it works:
A fluid, yoga-inspired move that builds strength, flexibility, and shoulder mobility.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, spine, and core.
How to do it:
- Start in downward dog position.
- Sweep your chest down and forward into upward dog.
- Reverse the motion to return.
Trainer Tip:
Breathe rhythmically and focus on smooth transitions for flexibility benefits.
19. Dive-Bomber Push-Up
Why it works:
A variant of the Hindu push-up emphasizing shoulders and spinal mobility.
Muscles worked:
Shoulders, chest, triceps, lower back, and hamstrings.
How to do it:
- Begin in a pike position.
- Lower your chest toward the floor, scooping into upward dog.
- Reverse the path back to start.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your core engaged and move smoothly — don’t rush.
20. Cross-Body Push-Up
Why it works:
Adds a rotational challenge that works obliques and improves core coordination.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, and obliques.
How to do it:
- As you lower, drive one knee across toward the opposite elbow.
- Return and switch sides each rep.
Trainer Tip:
Move deliberately and maintain tight abs to prevent twisting too much.
21. Offset Push-Up
Why it works:
The uneven hand placement increases range of motion and develops stabilizing muscles.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, and core.
How to do it:
- Place one hand on a small platform or medicine ball, the other on the floor.
- Perform a push-up, keeping your torso level.
- Alternate sides.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your shoulders even and control the descent — this prevents imbalance.
22. Typewriter Push-Up
Why it works:
Builds massive chest endurance and shoulder control through side-to-side motion.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, and abs.
How to do it:
- Start in a wide push-up position.
- Lower to one side, move laterally to the other side while staying low, then push back up.
Trainer Tip:
Stay controlled — avoid jerky movements. Quality beats quantity.
23. Superman Push-Up
Why it works:
Develops explosive strength and total-body coordination — ideal for athletes.
Muscles worked:
Chest, shoulders, triceps, abs, glutes, and lower back.
How to do it:
- Perform a push-up with enough power to lift both hands and feet off the floor.
- Land softly and reset before the next rep.
Trainer Tip:
Try partial explosive reps first before attempting full lift-off.
24. One-Arm Push-Up
Why it works:
A true test of strength and control — recruits every stabilizer in your core and upper body.
Muscles worked:
Chest, triceps, shoulders, abs, obliques.
How to do it:
- Spread your feet wide for balance.
- Place one hand under your chest.
- Lower down slowly and push back up powerfully.
Trainer Tip:
Practice archer push-ups first — they build strength needed for this move.
25. Handstand Push-Up
Why it works:
A challenging move that targets shoulders like an overhead press and strengthens the core and arms.
Muscles worked:
Shoulders, triceps, upper chest, traps, and core.
How to do it:
- Kick into a handstand against a wall.
- Lower your head toward the floor by bending elbows.
- Push back up to full lockout.
Trainer Tip:
Keep your spine neutral and use a folded mat under your head for safety.
Progression Plan: From Beginner to Pro
| Level | Focus | Recommended Variations |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Form & Endurance | Wall, Incline, Knee, Standard |
| Intermediate | Strength & Core | Decline, Spiderman, T Push-Up, Archer |
| Advanced | Power & Control | Plyometric, One-Arm, Handstand, Superman |
Trainer Tip:
Train 2–3 times weekly, performing 3–4 sets of 8–15 reps. Rest 60–90 seconds between sets.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Sagging hips – keep your core tight.
- Flaring elbows – maintain a 45° angle to prevent shoulder strain.
- Incomplete range of motion – lower until your chest nearly touches the floor.
- Rushing reps – focus on controlled movement.
Benefits of Mixing Push-Up Variations
- Builds balanced upper-body strength
- Enhances muscle definition and endurance
- Supports functional movement patterns
- Requires no equipment
- Improves athletic performance
Depending on body weight and pace, push-ups typically burn about 7–10 calories per minute; faster tempos and higher volumes trend toward the upper end of that range.
Sources: Harvard Health.
FAQs
1. Can beginners do push-up variations?
Yes. Start with wall or incline push-ups and progress gradually.
2. How many push-ups should I do daily?
Aim for 3 sets of 10–15 reps. Focus on form before increasing volume.
3. Do push-ups build muscle?
Yes — when performed with progressive variations and proper nutrition, they build lean upper-body muscle.
4. What muscles do push-ups work most?
Chest, triceps, shoulders, and core.
5. Are push-ups safe for shoulders?
Yes, if you maintain proper form and avoid excessive elbow flaring.
6. How can I make push-ups harder?
Add elevation, resistance bands, or explosive movements.
7. Should I do push-ups every day?
Not necessarily — rest at least one day between sessions to allow recovery.
Conclusion
Push-up variations are one of the most effective, equipment-free ways to build strength, improve balance, and sculpt your upper body. Whether you’re just starting or seeking new challenges, these 25 moves will help you progress safely and effectively.
Start with easier versions, master your form, and keep pushing your limits.
Consistency, not intensity, delivers long-term results.
References
- Cogley et al., 2005 — Hand Position & EMG
Comparison of muscle activation using various hand positions during the push-up exercise (J Strength Cond Res) — Narrow/diamond positions raise triceps and pec activation; perfect for your close-grip/diamond sections. - Calatayud et al., 2015 — Push-Up vs Bench Press
Bench press and push-up at comparable EMG levels produce similar strength gains (J Strength Cond Res) — Supports advanced programming (band-resisted push-ups can match bench strength outcomes). - van den Tillaar et al., 2019 — Push-Up vs Bench Kinematics/EMG
Comparison of kinematics and muscle activation between push-ups and bench press (Sports) — Shows movement/activation similarity, reinforcing transfer to pressing strength. - Ainsworth et al., 2011 — Compendium of Physical Activities (METs)
2011 Compendium (official table, PDF) — Provides MET values for calisthenics/push-ups to estimate intensity and calorie cost.
